VeA regulates conidiation, gliotoxin production, and protease activity in the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 23087369
- PMCID: PMC3536283
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00222-12
VeA regulates conidiation, gliotoxin production, and protease activity in the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
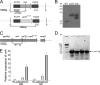
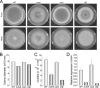
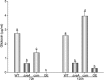
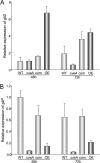
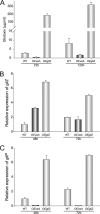
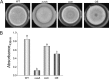
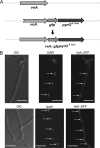
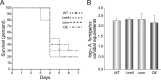
Invasive aspergillosis by Aspergillus fumigatus is a leading cause of infection-related mortality in immunocompromised patients. In this study, we show that veA, a major conserved regulatory gene that is unique to fungi, is necessary for normal morphogenesis in this medically relevant fungus. Although deletion of veA results in a strain with reduced conidiation, overexpression of this gene further reduced conidial production, indicating that veA has a major role as a regulator of development in A. fumigatus and that normal conidiation is only sustained in the presence of wild-type VeA levels. Furthermore, our studies revealed that veA is a positive regulator in the production of gliotoxin, a secondary metabolite known to be a virulent factor in A. fumigatus. Deletion of veA resulted in a reduction of gliotoxin production with respect to that of the wild-type control. This reduction in toxin coincided with a decrease in gliZ and gliP expression, which is necessary for gliotoxin biosynthesis. Interestingly, veA also influences protease activity in this organism. Specifically, deletion of veA resulted in a reduction of protease activity; this is the first report of a veA homolog with a role in controlling fungal hydrolytic activity. Although veA affects several cellular processes in A. fumigatus, pathogenicity studies in a neutropenic mouse infection model indicated that veA is dispensable for virulence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mtfA transcription factor gene controls morphogenesis, gliotoxin production, and virulence in the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Jun;13(6):766-75. doi: 10.1128/EC.00075-14. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24728192 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the gliP gene of Aspergillus fumigatus results in loss of gliotoxin production but has no effect on virulence of the fungus in a low-dose mouse infection model.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Oct;62(1):292-302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05373.x. Epub 2006 Aug 31. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16956378
-
The fumagillin gene cluster, an example of hundreds of genes under veA control in Aspergillus fumigatus.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 7;8(10):e77147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077147. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116213 Free PMC article.
-
What do we know about the role of gliotoxin in the pathobiology of Aspergillus fumigatus?Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S97-103. doi: 10.1080/13693780802056012. Epub 2008 May 2. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 18608908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic control of asexual development in aspergillus fumigatus.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2015;90:93-107. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25596030 Review.
Cited by
-
The velvet family of fungal regulators contains a DNA-binding domain structurally similar to NF-κB.PLoS Biol. 2013 Dec;11(12):e1001750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001750. Epub 2013 Dec 31. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 24391470 Free PMC article.
-
Extrolites of Aspergillus fumigatus and Other Pathogenic Species in Aspergillus Section Fumigati.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jan 7;6:1485. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01485. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26779142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two members of the velvet family, VmVeA and VmVelB, affect conidiation, virulence and pectinase expression in Valsa mali.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Jul;19(7):1639-1651. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12645. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29127722 Free PMC article.
-
The Aspergillus fumigatus UPR is variably activated across nutrient and host environments and is critical for the establishment of corneal infection.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Oct 31;19(10):e1011435. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011435. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37906600 Free PMC article.
-
Ochratoxin A Defective Aspergillus carbonarius Mutants as Potential Biocontrol Agents.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;14(11):745. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110745. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abad A, et al. 2010. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 27: 155–182 - PubMed
-
- Adams TH, Boylan MT, Timberlake WE. 1988. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 54: 353–362 - PubMed
-
- Araujo-Bazan L, et al. 2009. Importin alpha is an essential nuclear import carrier adaptor required for proper sexual and asexual development and secondary metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet. Biol. 46: 506–515 - PubMed
-
- Baba S, Kinoshita H, Nihira T. 2012. Identification and characterization of Penicillium citrinum VeA and LaeA as global regulators for ML-236B production. Curr. Genet. 58: 1–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

