Possible steps of complete disassembly of post-termination complex by yeast eEF3 deduced from inhibition by translocation inhibitors
- PMID: 23087377
- PMCID: PMC3592416
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks958
Possible steps of complete disassembly of post-termination complex by yeast eEF3 deduced from inhibition by translocation inhibitors
Abstract
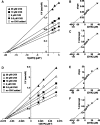
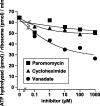
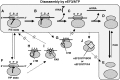
Ribosomes, after one round of translation, must be recycled so that the next round of translation can occur. Complete disassembly of post-termination ribosomal complex (PoTC) in yeast for the recycling consists of three reactions: release of tRNA, release of mRNA and splitting of ribosomes, catalyzed by eukaryotic elongation factor 3 (eEF3) and ATP. Here, we show that translocation inhibitors cycloheximide and lactimidomycin inhibited all three reactions. Cycloheximide is a non-competitive inhibitor of both eEF3 and ATP. The inhibition was observed regardless of the way PoTC was prepared with either release factors or puromycin. Paromomycin not only inhibited all three reactions but also re-associated yeast ribosomal subunits. On the other hand, sordarin or fusidic acid, when applied together with eEF2/GTP, specifically inhibited ribosome splitting without blocking of tRNA/mRNA release. From these inhibitor studies, we propose that, in accordance with eEF3's known function in elongation, the release of tRNA via exit site occurs first, then mRNA is released, followed by the splitting of ribosomes during the disassembly of post-termination complexes catalyzed by eEF3 and ATP.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Yeast translation elongation factor eEF3 promotes late stages of tRNA translocation.EMBO J. 2021 Mar 15;40(6):e106449. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020106449. Epub 2021 Feb 8. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33555093 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome recycling step in yeast cytoplasmic protein synthesis is catalyzed by eEF3 and ATP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 15;107(24):10854-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006247107. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534490 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of eEF3 and the mechanism of transfer RNA release from the E-site.Nature. 2006 Oct 12;443(7112):663-8. doi: 10.1038/nature05126. Epub 2006 Aug 23. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16929303
-
Dual functions of ribosome recycling factor in protein biosynthesis: disassembling the termination complex and preventing translational errors.Biochimie. 1996;78(11-12):959-69. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(97)86718-1. Biochimie. 1996. PMID: 9150873 Review.
-
The use of inhibitors in studies on protein synthesis.Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:261-82. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30030-4. Methods Enzymol. 1974. PMID: 4605358 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Ribosome profiling analysis of eEF3-depleted Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 28;9(1):3037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39403-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30816176 Free PMC article.
-
Toosendanin targeting eEF2 impedes Topoisomerase I & II protein translation to suppress esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 24;42(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02666-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37088855 Free PMC article.
-
Translational roles of elongation factor 2 protein lysine methylation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30511-30524. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605527. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25231983 Free PMC article.
-
Post-polyketide synthase steps in iso-migrastatin biosynthesis, featuring tailoring enzymes with broad substrate specificity.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Feb 20;135(7):2489-92. doi: 10.1021/ja4002635. Epub 2013 Feb 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23394593 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast translation elongation factor eEF3 promotes late stages of tRNA translocation.EMBO J. 2021 Mar 15;40(6):e106449. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020106449. Epub 2021 Feb 8. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33555093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirokawa G, Demeshkina N, Iwakura N, Kaji H, Kaji A. The ribosome-recycling step: consensus or controversy? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006;31:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Qin SL, Xie AG, Bonato MC, McLaughlin CS. Sequence analysis of the translational elongation factor 3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:1903–1912. - PubMed
-
- Triana-Alonso FJ, Chakraburtty K, Nierhaus KH. The elongation factor 3 unique in higher fungi and essential for protein biosynthesis is an E site factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:20473–20478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

