The Drosophila cyst stem cell lineage: Partners behind the scenes?
- PMID: 23087834
- PMCID: PMC3469438
- DOI: 10.4161/spmg.21380
The Drosophila cyst stem cell lineage: Partners behind the scenes?
Abstract
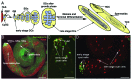
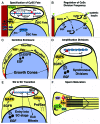
In all animals, germline cells differentiate in intimate contact with somatic cells and interactions between germline and soma are particularly important for germline development and function. In the male gonad of Drosophila melanogaster, the developing germline cells are enclosed by somatic cyst cells. The cyst cells are derived from cyst stem cells (CySCs) of somatic origin and codifferentiate with the germline cells. The fast generation cycle and the genetic tractability of Drosophila has made the Drosophila testis an excellent model for studying both the roles of somatic cells in guiding germline development and the interdependence of two separate stem cell lineages. This review focuses on our current understanding of CySC specification, CySC self-renewing divisions, cyst cell differentiation, and soma-germline interactions. Many of the mechanisms guiding these processes in Drosophila testes are similarly essential for the development and function of tissues in other organisms, most importantly for gametogenesis in mammals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch and Delta are required for survival of the germline stem cell lineage in testes of Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 12;14(9):e0222471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222471. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31513679 Free PMC article.
-
CSN maintains the germline cellular microenvironment and controls the level of stem cell genes via distinct CRLs in testes of Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Biol. 2015 Feb 1;398(1):68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.11.014. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25459658
-
Somatic CG6015 mediates cyst stem cell maintenance and germline stem cell differentiation via EGFR signaling in Drosophila testes.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Apr 6;7(1):68. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00452-w. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33824283 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental basis for germline mosaicism in mouse and Drosophila melanogaster.Genetica. 1998;102-103(1-6):421-43. Genetica. 1998. PMID: 9720293 Review.
-
Asymmetric divisions of germline cells.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2007;45:97-120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69161-7_5. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17585498 Review.
Cited by
-
The nuclear lamina regulates germline stem cell niche organization via modulation of EGFR signaling.Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Jul 3;13(1):73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.003. Cell Stem Cell. 2013. PMID: 23827710 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell autotomy and niche interaction in different systems.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Jul 26;7(6):922-44. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i6.922. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26240680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in Drosophila male germline stem cell biology.Spermatogenesis. 2012 Jul 1;2(3):137-144. doi: 10.4161/spmg.21763. Spermatogenesis. 2012. PMID: 23087833 Free PMC article.
-
Spermiogenesis and Male Fertility Require the Function of Suppressor of Hairy-Wing in Somatic Cyst Cells of Drosophila.Genetics. 2018 Jul;209(3):757-772. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301088. Epub 2018 May 8. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29739818 Free PMC article.
-
Reproduction disrupts stem cell homeostasis in testes of aged male Drosophila via an induced microenvironment.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jul 11;15(7):e1008062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008062. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31295251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huckins C. The spermatogonial stem cell population in adult rats. 3. Evidence for a long-cycling population. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1971;4:335–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
