Meiosis in male Drosophila
- PMID: 23087836
- PMCID: PMC3469440
- DOI: 10.4161/spmg.21800
Meiosis in male Drosophila
Abstract
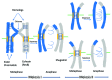
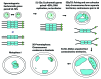
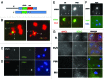
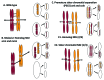
Meiosis entails sorting and separating both homologous and sister chromatids. The mechanisms for connecting sister chromatids and homologs during meiosis are highly conserved and include specialized forms of the cohesin complex and a tightly regulated homolog synapsis/recombination pathway designed to yield regular crossovers between homologous chromatids. Drosophila male meiosis is of special interest because it dispenses with large segments of the standard meiotic script, particularly recombination, synapsis and the associated structures. Instead, Drosophila relies on a unique protein complex composed of at least two novel proteins, SNM and MNM, to provide stable connections between homologs during meiosis I. Sister chromatid cohesion in Drosophila is mediated by cohesins, ring-shaped complexes that entrap sister chromatids. However, unlike other eukaryotes Drosophila does not rely on the highly conserved Rec8 cohesin in meiosis, but instead utilizes two novel cohesion proteins, ORD and SOLO, which interact with the SMC1/3 cohesin components in providing meiotic cohesion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cohesion protein SOLO associates with SMC1 and is required for synapsis, recombination, homolog bias and cohesion and pairing of centromeres in Drosophila Meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(7):e1003637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003637. Epub 2013 Jul 18. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23874232 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of cohesin proteins REC8, STAG3, SMC1 beta and SMC3 are consistent with a role in sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis in human oocytes.Hum Reprod. 2010 Sep;25(9):2316-27. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq180. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20634189
-
Pds5 is required for homologue pairing and inhibits synapsis of sister chromatids during yeast meiosis.J Cell Biol. 2009 Sep 7;186(5):713-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810107. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19736318 Free PMC article.
-
The nature of meiotic chromosome dynamics and recombination in budding yeast.J Microbiol. 2019 Apr;57(4):221-231. doi: 10.1007/s12275-019-8541-9. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30671743 Review.
-
The Role of Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes Complexes in Meiosis and Genome Maintenance: Translating Biomedical and Model Plant Research Into Crop Breeding Opportunities.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 31;12:659558. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.659558. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33868354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overview: Special issue on Drosophila spermatogenesis.Spermatogenesis. 2012 Jul 1;2(3):127-128. doi: 10.4161/spmg.21797. Spermatogenesis. 2012. PMID: 23087831 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetic breakdown of a Tet-off conditional lethality system for insect population control.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 18;11(1):3095. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16807-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32555259 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome interaction over a distance in meiosis.R Soc Open Sci. 2015 Feb 25;2(2):150029. doi: 10.1098/rsos.150029. eCollection 2015 Feb. R Soc Open Sci. 2015. PMID: 26064610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How and Why Chromosomes Interact with the Cytoskeleton during Meiosis.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 18;13(5):901. doi: 10.3390/genes13050901. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of male gametogenesis expressed genes from the scallop Nodipecten subnodosus by suppressive subtraction hybridization and pyrosequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e73176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073176. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066034 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
