Oral manifestations in type-2 diabetes and related complications
- PMID: 23087863
- PMCID: PMC3475903
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.100673
Oral manifestations in type-2 diabetes and related complications
Abstract
Background: Knowledge of the wide spectrum of the oral markers of diabetes is imperative as one frequently encounters individuals with undetected, untreated or poorly controlled diabetes.
Objectives: The objective was to study the oral manifestations in type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and to establish an association between oral manifestations and associated microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Materials and methods: 50 cases of DM were selected who had oral complications. The control group comprised 50 age- and sex-matched diabetic patients without any oral complications.
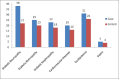
Results: Oral manifestations in DM included periodontal disease in 34%, oral candidiasis in 24%, tooth loss in 24%, oral mucosal ulcers in 22%, taste impairment in 20%, xerostomia and salivary gland hypofunction in 14%, dental caries in 24%, and burning mouth sensation in 10% cases. Fasting [(FBG) (P = 0.003)] and postprandial blood glucose [(PPBG) (P = 0.0003)] levels were significantly higher among cases. The P values for neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia, and sepsis were 0.0156, 0.0241, 0.68, 0.4047, 0.0278, and 0.3149, respectively, which were significant for neuropathy, retinopathy, and dyslipidemia.
Conclusions: Several oral complications are seen among diabetics. Association of oral markers in DM and microvascular complications suggests that there is a significant association between the two.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; dyslipidemia; neuropathy; oral complications; retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Grossi SG, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease and DM: A two-way relationship. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Terry DR. The diabetic dental patient. Dent Clin North Am. 1994;3:447–63. - PubMed
-
- Ship JA. Diabetes and oral health: An overview. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134:4S–10S. - PubMed
-
- Chandna S, Bathla M, Madaan V, Kalra S. Diabetes mellitus-a risk factor for periodontal disease. Internet J Fam Practice. 2010;9
-
- Shrimali L, Astekar M, Sowmya GV. Correlation of oral manifestations in diabetes mellitus. Int J Oral Max Pathol. 2011;27