Abrogating endocrine resistance by targeting ERα and PI3K in breast cancer
- PMID: 23087906
- PMCID: PMC3472546
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00145
Abrogating endocrine resistance by targeting ERα and PI3K in breast cancer
Abstract
Antiestrogen therapies targeting estrogen receptor α (ER) signaling are a mainstay for patients with ER+ breast cancer. While many cancers exhibit resistance to antiestrogen therapies, a large body of clinical and experimental evidence indicates that hyperactivation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway promotes antiestrogen resistance. In addition, continued ligand-independent ER signaling in the setting of estrogen deprivation may contribute to resistance to endocrine therapy. PI3K activates several proteins which promote cell cycle progression and survival. In ER+ breast cancer cells, PI3K promotes ligand-dependent and -independent ER transcriptional activity. Models of antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer often remain sensitive to estrogen stimulation and PI3K inhibition, suggesting that clinical trials with combinations of drugs targeting both the PI3K and ER pathways are warranted. Herein, we review recent findings on the roles of PI3K and ER in antiestrogen resistance, and clinical trials testing drug combinations which target both pathways. We also discuss the need for clinical investigation of ER downregulators in combination with PI3K inhibitors.
Keywords: PI3K; antiestrogen; aromatase; breast cancer; estrogen receptor; fulvestrant; tamoxifen.
Figures
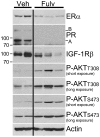
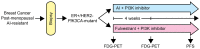
References
-
- Arpino G., Green S. J., Allred D. C., Lew D., Martino S., Osborne C. K., et al. (2004). HER-2 amplification, HER-1 expression, and tamoxifen response in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a southwest oncology group study. Clin. Cancer Res. 10 5670–5676 - PubMed
-
- Bachelot T., Bourgier C., Cropet C., Guastalla J.-P., Ferrero J.-M., Leger-Falandry C., et al. (2010). TAMRAD: a GINECO randomized phase II trial of everolimus in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone in patients (pts) with hormone-receptor positive, HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) with prior exposure to aromatase inhibitors (AI). Cancer Res. 70 abstract S1–S6 - PubMed
-
- Baselga J., Semiglazov V., Van Dam P., Manikhas A., Bellet M., Mayordomo J., et al. (2009). Phase II randomized study of neoadjuvant everolimus plus letrozole compared with placebo plus letrozole in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 27 2630–2637 - PubMed
-
- Campbell R. A., Bhat-Nakshatri P., Patel N. M., Constantinidou D., Ali S., Nakshatri H. (2001). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 276 9817–9824 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

