Relationship of copeptin, a surrogate marker for arginine vasopressin, with change in total kidney volume and GFR decline in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: results from the CRISP cohort
- PMID: 23089511
- PMCID: PMC3574620
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.08.038
Relationship of copeptin, a surrogate marker for arginine vasopressin, with change in total kidney volume and GFR decline in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: results from the CRISP cohort
Abstract
Background: Experimental studies indicate that arginine vasopressin (AVP) may have deleterious effects in the pathogenesis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). However, the significance of AVP in human ADPKD is unclear.
Study design: Longitudinal observational study with 8.5 (IQR, 7.7-9.0) years' follow-up (CRISP [Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Studies of Polycystic Kidney Disease]).
Setting & participants: 241 patients with ADPKD with creatinine clearance >70 mL/min.
Predictor: Plasma copeptin concentration, a surrogate marker for AVP.
Outcomes: Change in measured glomerular filtration rate (mGFR, assessed by iothalamate clearance) and total kidney volume (measured by magnetic resonance imaging).
Measurements: Baseline copeptin level, plasma and urinary osmolality, and measurements of total kidney volume and mGFR during follow-up.
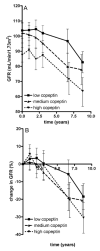
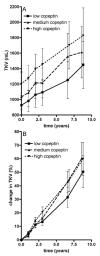
Results: In these patients (median age, 34 [IQR, 25-40] years; 38% men; median mGFR, 94 [IQR, 79-145] mL/min/1.73 m(2); median total kidney volume, 859 [IQR, 577-1,299] mL), median copeptin level was 2.9 (IQR, 1.8-5.1) pmol/L. Copeptin was not associated with plasma osmolality (P = 0.3), the physiologic stimulus for AVP release, but was associated significantly with change in total kidney volume during follow-up (P < 0.001). This association remained significant after adjusting for sex, age, cardiovascular risk factors, and diuretic use (P = 0.03). Copeptin level was associated borderline significantly with change in mGFR after adjusting for these variables (P = 0.09).
Limitations: No standardization of hydration status at time of copeptin measurement.
Conclusions: These data show that in ADPKD, copeptin level, as a marker for AVP, is not correlated with plasma osmolality. Most importantly, high copeptin levels are associated independently with disease progression in early ADPKD. This is in line with experimental studies that indicate a disease-promoting role for AVP.
Copyright © 2013 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369(9569):1287–1301. - PubMed
-
- Belibi FA, Reif G, Wallace DP, et al. Cyclic AMP promotes growth and secretion in human polycystic kidney epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2004;66(3):964–973. - PubMed
-
- Grantham JJ. Lillian Jean Kaplan International Prize for advancement in the understanding of polycystic kidney disease. Understanding polycystic kidney disease: a systems biology approach. Kidney Int. 2003;64(4):1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Morgenthaler NG, Struck J, Alonso C, Bergmann A. Assay for the measurement of copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the precursor of vasopressin. Clin Chem. 2006;52(1):112–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR00585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR23940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR023940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

