MHC class-I-restricted CD8 T cells play a protective role during primary Salmonella infection
- PMID: 23089550
- PMCID: PMC3540194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.10.009
MHC class-I-restricted CD8 T cells play a protective role during primary Salmonella infection
Abstract
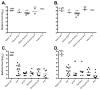
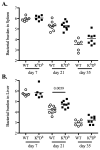
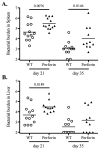
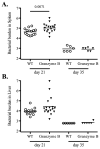
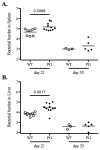
Protective immunity against Salmonella infection is known to require CD4 Th1 cells and B cells, but the role of MHC class-I-restricted CD8 T cells is less clear. Previous studies have suggested that CD8 T cells participate in secondary, but not primary, bacterial clearance. However, these studies have used experimental models that are difficult to interpret and do not clearly isolate the role of MHC class-I-restricted CD8 T cells from other cell populations. Here, we examined the role of class-I-restricted T cells in protection against Salmonella infection using mice lacking all classical MHC class-Ia molecules, perforin, or granzyme B. Immunized K(b)D(b)-, perforin-, granzyme B-, or perforin/granzyme B-deficient mice were able to resolve secondary infection with virulent Salmonella, demonstrating that class-I-restricted CTLs are not required for acquired immunity. However, during primary infection with attenuated bacteria, bacterial clearance was delayed in each of these mouse strains when compared to wild-type mice. Taken together, these data demonstrate that CD8 T cells are not required for acquired immunity to Salmonella, but can play a protective role in resolving primary infection with attenuated bacteria.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Both Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I (MHC-I) and MHC-II Molecules Are Required, while MHC-I Appears To Play a Critical Role in Host Defense against Primary Coxiella burnetii Infection.Infect Immun. 2018 Mar 22;86(4):e00602-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00602-17. Print 2018 Apr. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29311245 Free PMC article.
-
Nonconventional CD8+ T cell responses to Listeria infection in mice lacking MHC class Ia and H2-M3.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 1;186(1):489-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002639. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21098224 Free PMC article.
-
T cell responses to Gram-negative intracellular bacterial pathogens: a role for CD8+ T cells in immunity to Salmonella infection and the involvement of MHC class Ib molecules.J Immunol. 1999 May 1;162(9):5398-406. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10228017
-
Granzyme B regulates antiviral CD8+ T cell responses.J Immunol. 2011 Dec 15;187(12):6301-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100891. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22084442 Free PMC article.
-
The non-classical MHC class I molecule Qa-1(b) inhibits classical MHC class I-restricted cytotoxicity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Int Immunol. 2001 Mar;13(3):321-7. doi: 10.1093/intimm/13.3.321. Int Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11222501
Cited by
-
Salmonella escapes adaptive immune response via SIRT2 mediated modulation of innate immune response in dendritic cells.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Nov 19;14(11):e1007437. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007437. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30452468 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Biofilm Formation, Chronic Infection, and Immunity Within the Intestine and Hepatobiliary Tract.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 2;10:624622. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.624622. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33604308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteria That Cause Enteric Diseases Stimulate Distinct Humoral Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 16;11:565648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.565648. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium as a vaccine vector for HIV-1 Gag.Viruses. 2013 Aug 28;5(9):2062-78. doi: 10.3390/v5092062. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23989890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T Cell Immunity to Bacterial Pathogens: Mechanisms of Immune Control and Bacterial Evasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 26;21(17):6144. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176144. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32858901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

