Fully moderated T-statistic for small sample size gene expression arrays
- PMID: 23089813
- PMCID: PMC3192003
- DOI: 10.2202/1544-6115.1701
Fully moderated T-statistic for small sample size gene expression arrays
Abstract
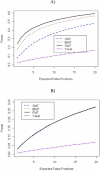
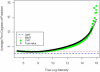
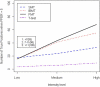
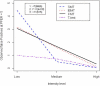
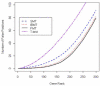
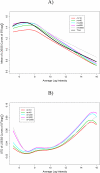
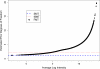
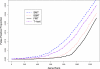
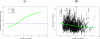
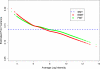
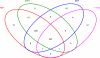
Gene expression microarray experiments with few replications lead to great variability in estimates of gene variances. Several Bayesian methods have been developed to reduce this variability and to increase power. Thus far, moderated t methods assumed a constant coefficient of variation (CV) for the gene variances. We provide evidence against this assumption, and extend the method by allowing the CV to vary with gene expression. Our CV varying method, which we refer to as the fully moderated t-statistic, was compared to three other methods (ordinary t, and two moderated t predecessors). A simulation study and a familiar spike-in data set were used to assess the performance of the testing methods. The results showed that our CV varying method had higher power than the other three methods, identified a greater number of true positives in spike-in data, fit simulated data under varying assumptions very well, and in a real data set better identified higher expressing genes that were consistent with functional pathways associated with the experiments.
Figures

References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. “Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing,”. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Cleveland WS. “Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots,”. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1979;74:829–836. doi: 10.2307/2286407. - DOI
-
- Cleveland WS, Devlin SJ. “Locally-weighted regression: An approach to regression analysis by local fitting,”. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 1988;83:596–610. doi: 10.2307/2289282. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
