Prostaglandin E2 regulates pancreatic stellate cell activity via the EP4 receptor
- PMID: 23090667
- PMCID: PMC3600062
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318264d0f8
Prostaglandin E2 regulates pancreatic stellate cell activity via the EP4 receptor
Abstract
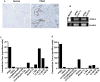
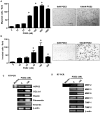
Objectives: Pancreatic stellate cells are source of dense fibrotic stroma, a constant pathological feature of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. We observed correlation between levels of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and its product prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and the extent of pancreatic fibrosis. The aims of this study were to delineate the effects of PGE2 on immortalized human pancreatic stellate cells (HPSCs) and to identify the receptor involved.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction were used to assess COX-2, extracellular matrix, and matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. Eicosanoid profile was determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Human pancreatic stellate cell proliferation was assessed by MTS assay, migration by Boyden chamber assay, and invasion using an invasion chamber. Transient silencing was obtained by small interfering RNA.
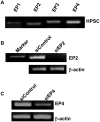
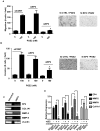
Results: Human pancreatic stellate cells express COX-2 and synthesize PGE2. Prostaglandin E2 stimulated HPSC proliferation, migration, and invasion and stimulated expression of both extracellular matrix and matrix metalloproteinase genes. Human pancreatic stellate cells expressed all 4 EP receptors. Only blocking the EP4 receptor resulted in abrogation of PGE2-mediated HPSC activation. Specificity of EP4 for the effects of PGE2 on stellate cells was confirmed using specific antagonists.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that PGE2 regulates pancreatic stellate cell profibrotic activities via EP4 receptor, thus suggesting EP4 receptor as useful therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer to reduce desmoplasia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 is involved in the cell growth and invasion of prostate cancer via the cAMP‑PKA/PI3K‑Akt signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Mar;17(3):4702-4712. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8415. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328471
-
Inhibitory effects of prostaglandin E2 on collagen synthesis and cell proliferation in human stellate cells from pancreatic head adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2014 Jun 9;14:413. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-413. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24912820 Free PMC article.
-
Direct growth-inhibitory effects of prostaglandin E2 in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro through an EP4/PKA-mediated mechanism.Surgery. 2017 Jun;161(6):1570-1578. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.12.037. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Surgery. 2017. PMID: 28222855 Free PMC article.
-
EP4 receptor as a novel promising therapeutic target in colon cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Dec;216(12):153247. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153247. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33190014 Review.
-
EP4 as a Therapeutic Target for Aggressive Human Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 29;19(4):1019. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041019. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29596308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Stellate Cells and the Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Pancreatitis.Molecules. 2023 Jul 22;28(14):5586. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145586. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Pancreatic Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Expression of Co-inhibitory Markers on CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 24;10:847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00847. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31068935 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 alters Wnt-dependent migration and proliferation in neuroectodermal stem cells: implications for autism spectrum disorders.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Mar 23;12:19. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-19. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 24656144 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and Regulation of Pancreatic Stellate Cells in Chronic Pancreatic Fibrosis: A Potential Therapeutic Approach for Chronic Pancreatitis.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 4;12(1):108. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010108. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic stellate cells and CX3CR1: occurrence in normal pancreas and acute and chronic pancreatitis and effect of their activation by a CX3CR1 agonist.Pancreas. 2014 Jul;43(5):708-19. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000109. Pancreas. 2014. PMID: 24681877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masamune A, Watanabe T, Kikuta K, et al. Roles of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:S48–54. - PubMed
-
- Vonlaufen A, Joshi S, Qu C, et al. Pancreatic stellate cells and pancreatic cancer cells: an unholy alliance. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2085–2093. - PubMed
-
- Apte MV, Wilson JS. Mechanisms of pancreatic fibrosis. Dig Dis. 2004;22:273–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

