MED12 mutations link intellectual disability syndromes with dysregulated GLI3-dependent Sonic Hedgehog signaling
- PMID: 23091001
- PMCID: PMC3511715
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1121120109
MED12 mutations link intellectual disability syndromes with dysregulated GLI3-dependent Sonic Hedgehog signaling
Abstract
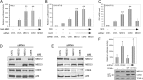
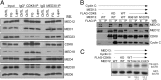
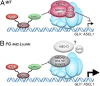
Recurrent missense mutations in the RNA polymerase II Mediator subunit MED12 are associated with X-linked intellectual disability (XLID) and multiple congenital anomalies, including craniofacial, musculoskeletal, and behavioral defects in humans with FG (or Opitz-Kaveggia) and Lujan syndromes. However, the molecular mechanism(s) underlying these phenotypes is poorly understood. Here we report that MED12 mutations R961W and N1007S causing FG and Lujan syndromes, respectively, disrupt a Mediator-imposed constraint on GLI3-dependent Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling. We show that the FG/R961W and Lujan/N1007S mutations disrupt the gene-specific association of MED12 with a second Mediator subunit, CDK8, identified herein to be a suppressor of GLI3 transactivation activity. In FG/R961W and Lujan/N1007S patient-derived cells, we document enhanced SHH pathway activation and GLI3-target gene induction coincident with impaired recruitment of CDK8 onto promoters of GLI3-target genes, but not non-GLI3-target genes. Together, these findings suggest that dysregulated GLI3-dependent SHH signaling contributes to phenotypes of individuals with FG and Lujan syndromes and further reveal a basis for the gene-specific manifestation of pathogenic mutations in a global transcriptional coregulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Yin and yang of mediator function revealed by human mutants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 27;109(48):19519-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217267109. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23184968 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rogers RC, Stevenson RE, Simensen RJ, Holden KR, Schwartz CE. Finding new etiologies of mental retardation and hypotonia: X marks the spot. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50(2):104–111. - PubMed
-
- Chiurazzi P, Schwartz CE, Gecz J, Neri G. XLMR genes: Update 2007. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16(4):422–434. - PubMed
-
- Risheg H, et al. A recurrent mutation in MED12 leading to R961W causes Opitz-Kaveggia syndrome. Nat Genet. 2007;39(4):451–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

