Does inflammation determine whether obesity is metabolically healthy or unhealthy? The aging perspective
- PMID: 23091306
- PMCID: PMC3471463
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/456456
Does inflammation determine whether obesity is metabolically healthy or unhealthy? The aging perspective
Abstract
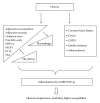
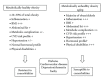
Obesity is a major health issue in developed as well as developing countries. While obesity is associated with relatively good health status in some individuals, it may become a health issue for others. Obesity in the context of inflammation has been studied extensively. However, whether obesity in its various forms has the same adverse effects is a matter of debate and requires further research. During its natural history, metabolically healthy obesity (MHO) converts into metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUHO). What causes this transition to occur and what is the role of obesity-related mediators of inflammation during this transition is discussed in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KGMM, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414(6865):782–787. - PubMed
-
- Evans AC, Papachristou GI, Whitcomb DC. Obesity and the risk of severe acute pancreatitis. Minerva Gastroenterologica e Dietologica. 2010;56(2):169–179. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H. The role of cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Digestive Diseases. 2010;28(1):179–185. - PubMed
-
- Andersson CX, Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Hedjazifar S, Smith U. Inflamed adipose tissue, insulin resistance and vascular injury. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews. 2008;24(8):595–603. - PubMed
-
- Gomes F, Telo DF, Souza HP, Nicolau JC, Halpern A, Serrano CV. Obesity and coronary artery disease: role of vascular inflammation. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia. 2010;94(2):255–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

