An intrathecally located broken catheter used for an intrathecal drug delivery system
- PMID: 23091331
- PMCID: PMC3468770
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.10.1278
An intrathecally located broken catheter used for an intrathecal drug delivery system
Abstract
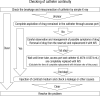
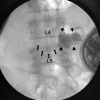
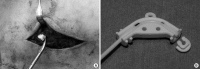
The intrathecal drug delivery system (ITDDS), an effective treatment tool for intractable spasticity and pain, is associated with various complications but breakage of the catheter is rare. We report the case of a 50-yr-old man with ITDDS, in whom an intrathecal catheter was severed, resulting in a 28.6-cm-long intrathecal fragment. The catheter completely retracted into the intrathecal space from the anchor site. The catheter was severed during spine flexion, and the total distal fragment was repositioned in the intrathecal space. Although the outcome of ITDDS was associated with the length or diameter of the broken catheter, no neurologic complications occurred in our patient. Thus, we inserted another catheter instead of removing the old one. Thereafter, the patient has been regularly followed up, and no neurologic complications have developed during the 28 months.
Keywords: Catheter; Complications; Implantable Infusion Pumps; Intrathecal Injections.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen SP, Dragovich A. Intrathecal analgesia. Anesthesiol Clin. 2007;25:863–882. viii. - PubMed
-
- Jones RL, Rawlins PK. The diagnosis of intrathecal infusion pump system failure. Pain Physician. 2005;8:291–296. - PubMed
-
- Ruan X. Drug-related side effects of long-term intrathecal morphine therapy. Pain Physician. 2007;10:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Williams BS, Christo PJ. Obstructed catheter connection pin discovered during intrathecal baclofen pump exchange. Clin J Pain. 2009;25:256–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

