Antihyperglycemic effects of fermented and nonfermented mung bean extracts on alloxan-induced-diabetic mice
- PMID: 23091343
- PMCID: PMC3469204
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/285430
Antihyperglycemic effects of fermented and nonfermented mung bean extracts on alloxan-induced-diabetic mice
Abstract
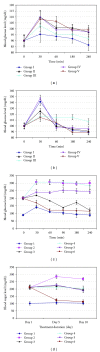
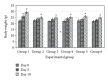
Mung bean was reported as a potential antidiabetic agent while fermented food has been proposed as one of the major contributors that can reduce the risk of diabetes in Asian populations. In this study, we have compared the normoglycemic effect, glucose-induced hyperglycemic effect, and alloxan-induced hyperglycemic effect of fermented and nonfermented mung bean extracts. Our results showed that fermented mung bean extracts did not induce hypoglycemic effect on normal mice but significantly reduced the blood sugar levels of glucose- and alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice. The serum levels of cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) were also lowered while insulin secretion and antioxidant level as measured by malonaldehyde (MDA) assays were significantly improved in the plasma of the fermented mung bean-treated group in alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mouse. These results indicated that fermentation using Mardi Rhizopus sp. strain 5351 inoculums could enhance the antihyperglycemic and the antioxidant effects of mung bean in alloxan-treated mice. The improvement in the antihyperglycemic effect may also be contributed by the increased content of GABA and the free amino acid that are present in the fermented mung bean extracts.
Figures
References
-
- Rungseesantivanon S, Thenchaisri N, Ruangvejvorachai P, Patumraj S. Curcumin supplementation could improve diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction associated with decreased vascular superoxide production and PKC inhibition. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2010;10, article 57 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwon DY, Daily JW, Kim HJ, Park S. Antidiabetic effects of fermented soybean products on type 2 diabetes. Nutrition Research. 2010;30(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Kameswararao B, Kesavulu MM, Apparao C. Evaluation of antidiabetic effect of Momordica cymbalaria fruit in alloxan-diabetic rats. Fitoterapia. 2003;74(1-2):7–13. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler ML. Nutrition management and physical activity as treatments for diabetes. Primary Care. 1999;26(4):857–868. - PubMed
-
- Reyes BAS, Bautista ND, Tanquilut NC, et al. Anti-diabetic potentials of Momordica charantia and andrographis paniculata and their effects on estrous cyclicity of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2006;105(1-2):196–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

