Efficacy of two novel 2,2'-bifurans to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in male mice in comparison to vancomycin
- PMID: 23091372
- PMCID: PMC3472655
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S36437
Efficacy of two novel 2,2'-bifurans to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in male mice in comparison to vancomycin
Abstract
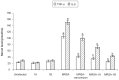
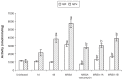
The therapeutic efficacy of two novel bifurans and vancomycin in an animal model of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection was compared. Adult male CF-1 mice (25-35 g) were intraperitoneally injected with 200 μL/mouse containing 10(7) cell-forming units of MRSA. After 16 hours, animals were treated with 110 mg/kg of vancomycin, or 5 mg/kg of mononitrile bifuran (1A) or monocationic bifuran (1B) and killed after 8 hours. Treatment with bifurans did not cause any toxicity. Treatment of MRSA-infected animals with bifurans resulted in significant reductions in the viable bacterial count in blood, liver, kidney, and spleen. Colonies recovered from livers and kidneys of mice injected with 1A or 1B lost the initial resistance pattern and became susceptible to methicillin and ciprofloxacin. MRSA elevated the serum urea level and activities of alanine aminotransferase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. MRSA also elevated the hepatic level of malondialdehyde, and serum levels of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6. MRSA also reduced the glutathione content and activities of catalase and glutathione S-transferase in liver. Similar to vancomycin, bifurans ameliorated most of the previous effects. Compound 1B was superior to 1A, and sometimes both provided better antistaphylococcal agents than vancomycin against MRSA pathogenesis. The present findings along with our previous studies support further evaluation of the efficacy of these bifurans in clinical studies.
Keywords: MRSA; antioxidants; bifuran derivatives; glutathione system; septicemia.
Figures
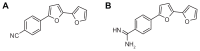


Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy of tigecycline VERSUS vancomycin in an experimental model of soft tissue infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus producing Panton-Valentine leukocidin.J Chemother. 2015 Feb;27(2):80-6. doi: 10.1179/1973947814Y.0000000171. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Chemother. 2015. PMID: 24548093
-
Reduced Vancomycin Susceptibility, MRSA and Treatment Failure in Pediatric Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021 May 1;40(5):429-433. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002992. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021. PMID: 33196562 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin treatment failure in a vancomycin susceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infected patient.Med J Malaysia. 2009 Jun;64(2):166-7. Med J Malaysia. 2009. PMID: 20058580
-
Alternative agents to vancomycin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Am J Ther. 2013 Mar-Apr;20(2):200-12. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31821109ec. Am J Ther. 2013. PMID: 21642833 Review.
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update on New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;34(4):849-861. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33011050 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel 4-substituted phenyl-2,2'-bichalcophenes and aza-analogs as antibacterial agents: a structural activity relationship.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013 Mar 22;7:185-93. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S42073. Print 2013. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 23662048 Free PMC article.
-
Antimutagenic and antioxidant activity of novel 4-substituted phenyl-2,2'-bichalcophenes and aza-analogs.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013;7:73-81. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S40129. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 23430305 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Insights of Fluoroaryl-2,2'-Bichalcophene Compounds on Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Molecules. 2020 Dec 30;26(1):139. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010139. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33396841 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the biological activity of novel monocationic fluoroaryl-2,2'-bichalcophenes and their analogues.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Jul 17;8:963-72. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S66469. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25114506 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, antimicrobial, and antiproliferative activities of substituted phenylfuranylnicotinamidines.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Mar 11;10:1133-46. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S102128. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27042005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kokai-Kun JF, Chanturiya T, Mond JJ. Lysostaphin as a treatment for systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection in a mouse model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:1051–1059. - PubMed
-
- Cantoni L, Wenger A, Glauser MP, Bille J. Comparative efficacy of amoxicillin-clavulanate, cloxacillin, and vancomycin against methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in rats. J Infect Dis. 1989;159:989–993. - PubMed
-
- Ismail MA, Arafa RK, Brun R, et al. Synthesis, DNA affinity, and antiprotozoal activity of linear dications: terphenyl diamidines and analogues. J Med Chem. 2006;49:5324–5332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

