The SCARB1 rs5888 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations
- PMID: 23091409
- PMCID: PMC3477681
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.4815
The SCARB1 rs5888 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations
Abstract
Background: The associations of scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SCARB1) rs5888 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and serum lipid levels are inconsistant among diverse ethnic populations. The present study was undertaken to detect the association of rs5888 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.
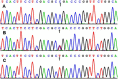
Methods: Genotypes of the SCARB1 rs5888 SNP in 801 subjects of Mulao and 807 subjects of Han Chinese were determined by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism combined with gel electrophoresis, and then confirmed by direct sequencing.
Results: Serum apolipoprotein (Apo) B levels and the T allelic frequency were higher in Mulao than in Han. Serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels in Mulao were different among the genotypes, the subjects with TT genotype had lower HDL-C levels than the subjects with CC or CT genotype in female (P < 0.05). For the Han population, serum triglyceride (TG), HDL-C, ApoAI, ApoB levels and the ratio of ApoAI to ApoB in males were different among the genotypes, the T allele carriers had lower serum HDL-C, ApoAI levels and ApoAI/ApoB ratio and higher serum ApoB levels than the T allele noncarriers (P < 0.05 for all), the subjects with TT genotype had higher serum TG levels than the subjects with CC or CT genotype. Serum HDL-C levels in Mulao females and serum HDL-C, ApoAI, ApoB levels and the ApoAI/ApoB ratio in Han males were correlated with genotypes by the multiple linear regression analysis. Serum lipid parameters were also influenced by genotype-environmental interactions in Han but not in Mulao populations.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the rs5888 SNP is associated with serum HDL-C levels in Mulao females, and TG, HDL-C, ApoAI, ApoB levels and the ApoAI/ApoB ratio in Han males. The differences in serum ApoB levels between the two ethnic groups might partially attribute to different SCARB1 genotype-environmental interactions.
Keywords: apolipoproteins; lipids; scavenger receptor class B type 1 gene; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of the KLF14 rs4731702 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:231515. doi: 10.1155/2013/231515. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24195066 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific association of rs16996148 SNP in the NCAN/CILP2/PBX4 and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 31;10:248. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-248. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22208664 Free PMC article.
-
Association of rs5888 SNP in the scavenger receptor class B type 1 gene and serum lipid levels.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Jul 9;11:50. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-50. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22583964 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the rs7395662 SNP in the MADD-FOLH1 and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Sep 1;10(11):1537-46. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6421. eCollection 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046529 Free PMC article.
-
Association of rs2072183 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 May 30;11:61. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-61. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22646906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of the KLF14 rs4731702 SNP and serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:231515. doi: 10.1155/2013/231515. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24195066 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the angiopoietin-like protein 8 rs2278426 polymorphism and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3285-3296. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3825. Epub 2015 May 25. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26004022 Free PMC article.
-
Association of rs5888 SNP in SCARB1 gene with coronary artery disease : Study of a Han Chinese population.Herz. 2019 Nov;44(7):644-650. doi: 10.1007/s00059-018-4689-z. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Herz. 2019. PMID: 29516118 English.
-
Association of two polymorphisms in the FADS1/FADS2 gene cluster and the risk of coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7318-31. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261632 Free PMC article.
-
The rs5888 single nucleotide polymorphism in scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SCARB1) gene and the risk of premature coronary artery disease: a case-control study.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Jan 12;15:7. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0176-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 26754576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M. et al. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–57. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW. High-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein and coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990;66:7A–10A. - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP, Garrison RJ, Wilson PW. et al. Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The Framingham Study. JAMA. 1986;256:2835–8. - PubMed
-
- Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ. et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation. 1989;79:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Heller DA, de Faire U, Pedersen NL. et al. Genetic and environmental influences on serum lipid levels in twins. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1150–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

