Hair Analysis for Determination of Isoniazid Concentrations and Acetylator Phenotype during Antituberculous Treatment
- PMID: 23091716
- PMCID: PMC3469096
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/327027
Hair Analysis for Determination of Isoniazid Concentrations and Acetylator Phenotype during Antituberculous Treatment
Abstract
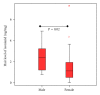
Background. Analysis of isoniazid (INH) uptake has been based on measurement of plasma concentrations providing a short-term and potentially biased view. Objectives. To establish hair analysis as a tool to measure long-term uptake of INH and to assess whether acetylator phenotype in hair reflects N-acetyltransferase-2 (NAT2) genotype. Design and Methods. INH and acetyl-INH concentrations in hair were determined in patients on INH treatment for M. tuberculosis infection using high pressure liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Acetyl-INH/INH ratios were correlated with NAT-2 genotype. Results. Hair concentrations of INH, determined in 40 patients, were not dependent on ethnic group or body mass index and were significantly higher in male compared to female patients (median (range) 2.37 ng/mg (0.76-4.9) versus 1.11 ng/mg (0.02-7.20) (P = 0.02). Acetyl-INH/INH ratios were a median of 15.2% (14.5 to 31.7) in homozygous rapid acetylator NAT-2 genotype and 37.3% (1.73 to 51.2) in the heterozygous rapid acetylator NAT-2 genotype and both significantly higher than in the slow acetylator NAT-2 genotype with 5.8% (0.53 to 14.4) (P < 0.05). Conclusions. Results of hair analysis for INH showed lower concentrations in females. Acetyl-INH/INH ratios were significantly lower in patients with slow acetylator versus rapid acetylator genotypes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Influence of NAT2 Genotypes on Isoniazid Plasma Concentration of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients in Southern Thailand.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2020 Dec;83(Supple 1):S55-S62. doi: 10.4046/trd.2020.0068. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 33138342 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic characterization of acetylator genotype-dependent and -independent N-acetyltransferase isozymes in homozygous rapid and slow acetylator inbred hamster liver cytosol.Drug Metab Dispos. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):238-47. Drug Metab Dispos. 1989. PMID: 2568903
-
Anthropometric and Genetic Factors Associated With the Exposure of Rifampicin and Isoniazid in Mexican Patients With Tuberculosis.Ther Drug Monit. 2019 Oct;41(5):648-656. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000631. Ther Drug Monit. 2019. PMID: 30939588
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Isoniazid Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Tuberculosis.Clin Ther. 2020 Nov;42(11):e220-e241. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 33032843
-
Acetylation.Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1990;26(1):43-65. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1990. PMID: 2224079 Review.
Cited by
-
Isoniazid hair concentrations in children with tuberculosis: a proof of concept study.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016 Jun;20(6):844-7. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.15.0882. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016. PMID: 27155191 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Methods for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Dose Adjustment of Tuberculosis Treatment in Clinical Settings: A Systematic Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023 Mar;62(3):375-398. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01220-y. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023. PMID: 36869170 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of physiological characteristics, smoking, and alcohol use on isoniazid hair drug levels among pulmonary TB patients: a cross-sectional study at one month of intensive TB treatment.Afr Health Sci. 2025 Jun;25(2):1-9. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v25i2.2. Afr Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 40837662 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Isoniazid Levels in Small Hair Samples: A Novel Method for Assessing Adherence during the Treatment of Latent and Active Tuberculosis.PLoS One. 2016 May 18;11(5):e0155887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155887. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27191185 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous analysis of 11 medications for drug resistant TB in small hair samples to quantify adherence and exposure using a validated LC-MS/MS panel.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;1125:121729. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121729. Epub 2019 Jul 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31369929 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bernard L, Vuagnat A, Peytavin G, et al. Relationship between levels of indinavir in hair and virologic response to highly active antiretroviral therapy. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;137(8):656–659. - PubMed
-
- Williams J, Patsalos PN, Wilson JF. Hair analysis as a potential index of therapeutic compliance in the treatment of epilepsy. Forensic Science International. 1997;84(1–3):113–122. - PubMed
-
- Donald PR, Parkin DP, Seifart HI, et al. The influence of dose and N-acetyltransferase-2 (NAT2) genotype and phenotype on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of isoniazid. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2007;63(7):633–639. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

