Th17 mediated alloreactivity is facilitated by the pre-transplant microbial burden of the recipient
- PMID: 23091728
- PMCID: PMC3472510
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/960280
Th17 mediated alloreactivity is facilitated by the pre-transplant microbial burden of the recipient
Abstract
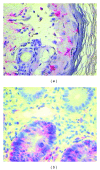
Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) is a major complication after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and severity of aGvHD is associated with biological and genetic factors related to donors and recipients. Studies on inflammatory pathways involved in aGvHD have shown a significant impact of the gut microflora on aGvHD development giving increasing evidence in the understanding of the response of innate and adaptive immunity to microbial products. Cytokine deregulation may increase or reduce the risk of aGvHD. Damage of tissues affected by aGvHD reflects the immunological cascade of events in this disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allogenic stem cell transplant-associated acute graft versus host disease: a computational drug discovery text mining approach using oral and gut microbiome signatures.Support Care Cancer. 2021 Apr;29(4):1765-1779. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05821-2. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Support Care Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33094358 Review.
-
Homing in on acute graft vs. host disease: tissue-specific T regulatory and Th17 cells.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;341:121-46. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_24. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20563712 Free PMC article.
-
Pretransplant donor and recipient CTLA-4 mRNA and protein levels as a prognostic marker for aGvHD in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Immunol Lett. 2015 May;165(1):52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Immunol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25841352
-
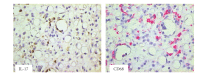
The expression of Th17-associated cytokines in human acute graft-versus-host disease.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013 Oct;19(10):1421-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23792271
-
How to Make an Immune System and a Foreign Host Quickly Cohabit in Peace? The Challenge of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Prevention After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 21;11:583564. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583564. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Activity of IL-17+ Cells in Chronic Skin and Mucosa Graft-Versus-Host Disease.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019 Oct;67(5):311-323. doi: 10.1007/s00005-019-00549-2. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019. PMID: 31177288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett AJ. Understanding and harnessing the graft-versus-leukaemia effect. British Journal of Haematology. 2008;142(6):877–888. - PubMed
-
- Prasad VK, Kurtzberg J. Cord blood and bone marrow transplantation in inherited metabolic diseases: scientific basis, current status and future directions. British Journal of Haematology. 2010;148(3):356–372. - PubMed
-
- Sackstein R. A revision of Billingham’s tenets: the central role of lymphocyte migration in acute graft-versus-host disease. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2006;12(1):2–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

