Acute gastrointestinal syndrome in high-dose irradiated mice
- PMID: 23091876
- PMCID: PMC3530834
- DOI: 10.1097/hp.0b013e318266ee13
Acute gastrointestinal syndrome in high-dose irradiated mice
Abstract
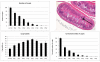
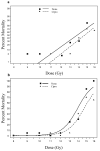
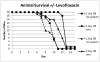
The most detailed reports of the response of the gastrointestinal system to high dose acute radiation have focused mainly on understanding the histopathology. However, to enable medical countermeasure assessment under the animal rule criteria, it is necessary to have a robust model in which the relationship between radiation dose and intestinal radiation syndrome incidence, timing, and severity are established and correlated with histopathology. Although many mortality studies have been published, they have used a variety of mouse strains, ages, radiation sources, and husbandry conditions, all of which influence the dose response. Further, it is clear that the level of bone marrow irradiation and supportive care can influence endpoints. In order to create robust baseline data, the authors have generated dose response data in adult male mice maintained under identical conditions and exposed to either total or partial-body irradiation. Partial-body irradiation includes both extensive (40%) and minimal (5%) bone marrow sparing models, the latter designed to correlate with an established primate model and allow assessment of effects of any medical countermeasure on all three major radiation syndromes (intestinal, bone marrow, and lung) in the surviving mice. Lethal dose (LD(30), LD(50), and LD(70)) data are described in the various models, along with the impact of enteric flora and response to supportive care. Correlation with diarrhea severity and histopathology are also described. These data can be used to aid the design of good laboratory practice (GLP)-compliant Animal Rule studies that are reflective of the conditions following accidental radiation exposure.
Figures





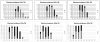




References
-
- Boggs DR. The total marrow mass of the mouse: a simplified method of measurement. Am J Hematol. 1984;16(3):277–286. - PubMed
-
- Booth C, Potten CS. The Intestine as a Model for Studying Stem Cell Behaviour. In: Teicher BA, editor. Tumor Models in Cancer Research. Humana Press; Totawa, New Jersey: 2001a. pp. 337–357.
-
- Booth D, Potten CS. Protection against mucosal injury by growth factors and cytokines. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2001b;29:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Booth D, Haley JD, Bruskin AM, Potten CS. Transforming growth factor beta 3 protects murine small intestinal crypt stem cells and animal survival after irradiation, possibly by reducing stem cell cycling. Int J Cancer. 2000;86(1):53–59. - PubMed
-
- Cai WB, Roberts SA, Potten CS. The number of clonogenic cells in crypts in three regions of murine large intestine. Int J Radiat Biol. 1997a;71(5):573–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

