Novel directions for diabetes mellitus drug discovery
- PMID: 23092114
- PMCID: PMC3529804
- DOI: 10.1517/17460441.2013.736485
Novel directions for diabetes mellitus drug discovery
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus impacts almost 200 million individuals worldwide and leads to debilitating complications. New avenues of drug discovery must target the underlying cellular processes of oxidative stress, apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation that can mediate multi-system pathology during diabetes mellitus.
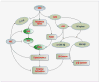
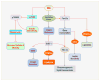
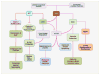
Areas covered: The authors examine the novel directions for drug discovery that involve: the β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) precursor nicotinamide, the cytokine erythropoietin, the NAD(+)-dependent protein histone deacetylase SIRT1, the serine/threonine-protein kinase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the wingless pathway. Furthermore, the authors present the implications for the targeting of these pathways that oversee gluconeogenic genes, insulin signaling and resistance, fatty acid beta-oxidation, inflammation, and cellular survival.
Expert opinion: Nicotinamide, erythropoietin, and the downstream pathways of SIRT1, mTOR, forkhead transcription factors, and wingless signaling offer exciting prospects for novel directions of drug discovery for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Future investigations must dissect the complex relationship and fine modulation of these pathways for the successful translation of robust reparative and regenerative strategies against diabetes mellitus and the complications of this disorder.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah A, Wolfe R, Mannan H, et al. Epidemiologic Merit of Obese-Years, the Combination of Degree and Duration of Obesity. Am J Epidemiol. 2012 Jun 28; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
