Unchanged severity of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection in children during first postpandemic season
- PMID: 23092713
- PMCID: PMC3559159
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1811.120719
Unchanged severity of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection in children during first postpandemic season
Abstract
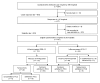
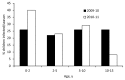
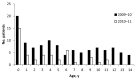
We conducted a nationwide hospital-based prospective study in Germany of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 cases among children <15 years of age admitted to pediatric intensive care units and related deaths during the 2009-10 pandemic and the 2010-11 postpandemic influenza seasons. We identified 156 eligible patients: 112 in 2009-10 and 44 in 2010-11. Although a shift to younger patients occurred in 2010-11 (median age 3.2 vs. 5.3 years), infants <1 year of age remained the most affected. Underlying immunosuppression was a risk factor for hospital-acquired infections (p = 0.013), which accounted for 14% of cases. Myocarditis was predictive of death (p = 0.006). Of the 156 case-patients, 17% died; the difference between seasons was not significant (p = 0.473). Our findings stress the challenge of preventing severe postpandemic influenza infection in children and the need to prevent nosocomial transmission of influenza virus, especially in immunosuppressed children.
Figures

References
-
- Robert Koch Institute. Report on Influenza epidemiology in Germany, 2009–10 season [in German] [cited 2012 May 2]. http://influenza.rki.de/Saisonberichte/2009.pdf
-
- Robert Koch-Institute. Influenza-Weekly Report, Germany, 2010. [in German] [cited 2012 May 2]. http://influenza.rki.de/Wochenberichte/2009_2010/2010-31.pdf
-
- Wilking H, Buda S, von der Lippe E, Altmann D, Krause G, Eckmanns T, et al. Mortality of 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) in Germany. Euro Surveill. 2010;15:19741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
