Defective postnatal endochondral bone development by chondrocyte-specific targeted expression of parathyroid hormone type 2 receptor
- PMID: 23092913
- PMCID: PMC3532463
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00254.2012
Defective postnatal endochondral bone development by chondrocyte-specific targeted expression of parathyroid hormone type 2 receptor
Abstract
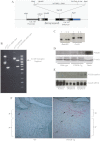
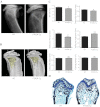
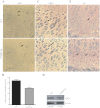
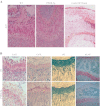
The human parathyroid hormone type 2 receptor (PTH2R) is activated by PTH and by tuberoinfundibular peptide of 39 residues (TIP39), the latter likely acting as its natural ligand. Although the receptor is expressed at highest levels in the nervous system, we have observed that both PTH2R and TIP39 are expressed in the newborn mouse growth plate, with the receptor localizing in the resting zone and the ligand TIP39 localizing exclusively in prehypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes. To address the role of PTH2R in postnatal skeletal growth and development, Col2a1-hPTH2R (PTH2R-Tg) transgenic mice were generated. The mice were viable and of nearly normal size at birth. Expression of the transgene in the growth plate was limited to chondrocytes. We found that chondrocyte proliferation was decreased, as determined by in vivo BrdU labeling of proliferating chondrocytes and CDK4 and p21 expression in the growth plate of Col2a1-hPTH2R transgenic mice. Similarly, the differentiation and maturation of chondrocytes was delayed, as characterized by decreased Sox9 expression and weaker immunostaining for the chondrocyte differentiation markers collagen type II and type X and proteoglycans. As well, there was altered expression of Gdf5, Wdr5, and β-catenin, factors implicated in chondrocyte maturation, proliferation, and differentiation.These effects impacted on the process of endochondral ossification, resulting in delayed formation of the secondary ossification center, and diminished trabecular bone volume. The findings substantiate a role for PTH2R signaling in postnatal growth plate development and subsequent bone mass acquisition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TIP39/parathyroid hormone type 2 receptor signaling is a potent inhibitor of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Nov;297(5):E1125-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00254.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19706789 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted expression of SHH affects chondrocyte differentiation, growth plate organization, and Sox9 expression.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Oct;19(10):1678-88. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040706. Epub 2004 Jul 12. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15355563
-
Core binding factor beta (Cbfβ) controls the balance of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation by upregulating Indian hedgehog (Ihh) expression and inhibiting parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor (PPR) expression in postnatal cartilage and bone formation.J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Jul;29(7):1564-1574. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2275. J Bone Miner Res. 2014. PMID: 24821091 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional mechanisms of chondrocyte differentiation.Matrix Biol. 2000 Sep;19(5):389-94. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(00)00094-9. Matrix Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980415 Review.
-
The chondrocytic journey in endochondral bone growth and skeletal dysplasia.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014 Mar;102(1):52-73. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21060. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014. PMID: 24677723 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of the PH-domain and Leucine-rich Repeat Protein Phosphatase 1 (Phlpp1) Increases Fibroblast Growth Factor (Fgf) 18 Expression and Promotes Chondrocyte Proliferation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 26;290(26):16272-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.612937. Epub 2015 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25953896 Free PMC article.
-
Breakpoint mapping by whole genome sequencing identifies PTH2R gene disruption in a patient with midline craniosynostosis and a de novo balanced chromosomal rearrangement.J Med Genet. 2015 Oct;52(10):706-9. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103001. Epub 2015 Jun 4. J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26044810 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese Medicinal Formulation Guzhi Zengsheng Zhitongwan Modulates Chondrocyte Structure, Dynamics, and Metabolism by Controlling Multiple Functional Proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Nov 22;2018:9847286. doi: 10.1155/2018/9847286. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30596102 Free PMC article.
-
The Parathyroid Hormone Second Receptor PTH2R and its Ligand Tuberoinfundibular Peptide of 39 Residues TIP39 Regulate Intracellular Calcium and Influence Keratinocyte Differentiation.J Invest Dermatol. 2016 Jul;136(7):1449-1459. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.02.814. Epub 2016 Mar 19. J Invest Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27000502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou-Samra AB, Jüppner H, Force T, Freeman MW, Kong XF, Schipani E, Urena P, Richards J, Bonventre JV, Potts JT, Jr, Kronenberg HM, Segre GV. Expression cloning of a common receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide from rat osteoblast-like cells: a single receptor stimulates intracellular accumulation of both cAMP and inositol trisphosphates and increases intracellular free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 2732–2736, 1992 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell DM, Leung KK, Wheatley SC, Ng LJ, Zhou S, Ling KW, Sham MH, Koopman P, Tam PP, Cheah KS. SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet 16: 174–178, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Blumer MJ, Longato S, Fritsch H. Structure, formation and role of cartilage canals in the developing bone. Ann Anat 190: 305–315, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Buxton P, Edwards C, Archer CW, Francis-West P. Growth/differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) and skeletal development. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A, Suppl 1: S23–S30, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

