Interleukin-6 production in CD40-engaged fibrocytes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: involvement of Akt and NF-κB
- PMID: 23092922
- PMCID: PMC3506052
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-9861
Interleukin-6 production in CD40-engaged fibrocytes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: involvement of Akt and NF-κB
Abstract
Purpose: CD40-CD40 ligand (CD40L) interactions appear to play pathogenic roles in autoimmune disease. Here we quantify CD40 expression on fibrocytes, circulating, and bone marrow-derived progenitor cells. The functional consequences of CD40 ligation are determined since these may promote tissue remodeling linked with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO).
Methods: CD40 levels on cultivated fibrocytes and orbital fibroblasts (GOFB) from patients with Graves' disease (GD), as well as fibrocyte abundance, were determined by flow cytometry. CD40 mRNA expression was evaluated by real-time PCR, whereas response to CD40 ligation was measured by Luminex and RT-PCR. Protein kinase B (Akt) and nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling were determined by Western blot and immunofluorescence.
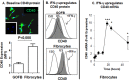
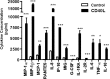
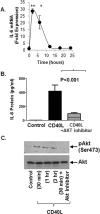
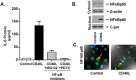
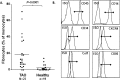
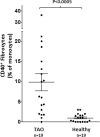
Results: Basal CD40 expression on fibrocytes is greater than that on GOFB. IFN-γ upregulates CD40 in both cell types and its actions are mediated at the pretranslational level. Fibrocytes produce high levels of cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), TNF-α, IL-8, MCP-1, and RANTES (Regulated on Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Secreted) in response to CD40L. IL-6 induction results from an increase in steady state IL-6 mRNA, and is mediated through Akt and NF-κB activation. Circulating CD40(+)CD45(+)Col1(+) fibrocytes are far more frequent in vivo in donors with TAO compared with healthy subjects.
Conclusions: Particularly high levels of functional CD40 are displayed by fibrocytes. CD40L-provoked signaling results in the production of several cytokines. Among these, IL-6 expression is mediated through Akt and NF-κB pathways. The frequency of circulating CD40(+) fibrocytes is markedly increased in patients with TAO, suggesting that this receptor might represent a therapeutic target for TAO.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thyrotropin receptor and CD40 mediate interleukin-8 expression in fibrocytes: implications for thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;112:26-37. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25411513 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A Promotes RANTES Expression, But Not IL-16, in Orbital Fibroblasts Via CD40-CD40L Combination in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Nov 1;57(14):6123-6133. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20199. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27832278
-
Thyrotropin and CD40L Stimulate Interleukin-12 Expression in Fibrocytes: Implications for Pathogenesis of Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.Thyroid. 2016 Dec;26(12):1768-1777. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0243. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Thyroid. 2016. PMID: 27612658 Free PMC article.
-
[Bone marrow-derived fibrocytes and thyroid-associated opthalmopathy].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 11;53(6):470-473. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2017.06.017. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28606271 Review. Chinese.
-
Potential Roles of CD34+ Fibrocytes Masquerading as Orbital Fibroblasts in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Feb 1;104(2):581-594. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01493. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30445529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TSHR Signaling Stimulates Proliferation Through PI3K/Akt and Induction of miR-146a and miR-155 in Thyroid Eye Disease Orbital Fibroblasts.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Oct 1;60(13):4336-4345. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-27865. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31622470 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes in corticosteroid-refractory Graves' orbitopathy treated with tocilizumab.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022 Sep;97(3):363-370. doi: 10.1111/cen.14655. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 34908176 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of fibrocytes in ocular disorders.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Apr 13;9(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0835-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29653588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of cytokine production by drugs with antiepileptic or mood stabilizer properties in anti-CD3- and anti-Cd40-stimulated blood in vitro.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:806162. doi: 10.1155/2014/806162. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24757498 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SerpinA3 in the Pathogenesis of Graves' Orbitopathy in Orbital Fibroblasts.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Apr 1;66(4):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.4.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40202736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valle A, Zuber CE, Defrance T, Djossou O, De Rie M, Banchereau J. Activation of human B lymphocytes through CD40 and interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:1463–1467 - PubMed
-
- Cosman D. A family of ligands for the TNF receptor superfamily. Stem Cells. 1994;12:440–455 - PubMed
-
- Smith TJ, Sciaky D, Phipps RP, Jennings TA. CD40 expression in human thyroid tissue: evidence for involvement of multiple cell types in autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Thyroid. 1999;9:749–755 - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Fiocchi C. Platelet activation and the CD40/CD40 ligand pathway: mechanisms and implications for human disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 2005;25:103–121 - PubMed
-
- Fries KM, Sempowski GD, Gaspari AA, Blieden T, Looney RJ, Phipps RP. CD40 expression by human fibroblasts. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;77:42–51 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 EY016339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY021197/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY007003/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY021197/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 EY011708/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY011708/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY016339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY007003/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY008976/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063121/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY008976/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 EY007003/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK063121/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

