SUMOylation of hnRNP-K is required for p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest in response to DNA damage
- PMID: 23092970
- PMCID: PMC3512394
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.293
SUMOylation of hnRNP-K is required for p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest in response to DNA damage
Abstract
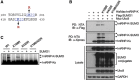
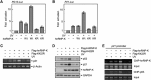
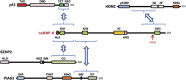
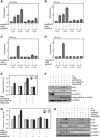
Heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein-K (hnRNP-K) is normally ubiquitinated by HDM2 for proteasome-mediated degradation. Under DNA-damage conditions, hnRNP-K is transiently stabilized and serves as a transcriptional co-activator of p53 for cell-cycle arrest. However, how the stability and function of hnRNP-K is regulated remained unknown. Here, we demonstrated that UV-induced SUMOylation of hnRNP-K prevents its ubiquitination for stabilization. Using SUMOylation-defective mutant and purified SUMOylated hnRNP-K, SUMOylation was shown to reduce hnRNP-K's affinity to HDM2 with an increase in that to p53 for p21-mediated cell-cycle arrest. PIAS3 served as a small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) E3 ligase for hnRNP-K in an ATR-dependent manner. During later periods after UV exposure, however, SENP2 removed SUMO from hnRNP-K for its destabilization and in turn for release from cell-cycle arrest. Consistent with the rise-and-fall of both SUMOylation and stability of hnRNP-K, its ability to interact with PIAS3 was inversely correlated to that with SENP2 during the time course after UV exposure. These findings indicate that SUMO modification plays a crucial role in the control of hnRNP-K's function as a p53 co-activator in response to DNA damage by UV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abraham RT (2001) Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev 15: 2177–2196 - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT (2004) PI 3-kinase related kinases: 'big' players in stress-induced signaling pathways. DNA Repair (Amst) 3: 883–887 - PubMed
-
- Baptiste-Okoh N, Barsotti AM, Prives C (2008) Caspase 2 is both required for p53-mediated apoptosis and downregulated by p53 in a p21-dependent manner. Cell Cycle 7: 1133–1138 - PubMed
-
- Bartek J, Lukas J (2001) Mammalian G1- and S-phase checkpoints in response to DNA damage. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13: 738–747 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

