Nature or nurture? Determining the heritability of human striatal dopamine function: an [18F]-DOPA PET study
- PMID: 23093224
- PMCID: PMC3547199
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.207
Nature or nurture? Determining the heritability of human striatal dopamine function: an [18F]-DOPA PET study
Abstract
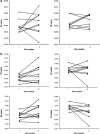
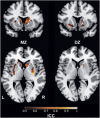
Striatal dopamine function is important for normal personality, cognitive processes and behavior, and abnormalities are linked to a number of neuropsychiatric disorders. However, no studies have examined the relative influence of genetic inheritance and environmental factors in determining striatal dopamine function. Using [18F]-DOPA positron emission tomography (PET), we sought to determine the heritability of presynaptic striatal dopamine function by comparing variability in uptake values in same sex monozygotic (MZ) twins to dizygotic (DZ) twins. Nine MZ and 10 DZ twin pairs underwent high-resolution [18F]-DOPA PET to assess presynaptic striatal dopamine function. Uptake values for the overall striatum and functional striatal subdivisions were determined by a Patlak analysis using a cerebellar reference region. Heritability, shared environmental effects and non-shared individual-specific effects were estimated using a region of interest (ROI) analysis and a confirmatory parametric analysis. Overall striatal heritability estimates from the ROI and parametric analyses were 0.44 and 0.33, respectively. We found a distinction between striatal heritability in the functional subdivisions, with the greatest heritability estimates occurring in the sensorimotor striatum and the greatest effect of individual-specific environmental factors in the limbic striatum. Our results indicate that variation in overall presynaptic striatal dopamine function is determined by a combination of genetic factors and individual-specific environmental factors, with familial environmental effects having no effect. These findings underline the importance of individual-specific environmental factors for striatal dopaminergic function, particularly in the limbic striatum, with implications for understanding neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and addictions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of non-genetic factors to dopamine and serotonin receptor availability in the adult human brain.Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Aug;21(8):1077-84. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.147. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26821979
-
The test-retest reliability of 18F-DOPA PET in assessing striatal and extrastriatal presynaptic dopaminergic function.Neuroimage. 2010 Apr 1;50(2):524-531. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.058. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20034580 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced striatal dopamine synthesis capacity in patients with schizophrenia during remission of positive symptoms.Brain. 2019 Jun 1;142(6):1813-1826. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz093. Brain. 2019. PMID: 31135051
-
Aberrant striatal dopamine links topographically with cortico-thalamic dysconnectivity in schizophrenia.Brain. 2020 Dec 5;143(11):3495-3505. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa296. Brain. 2020. PMID: 33155047
-
Molecular imaging studies of the striatal dopaminergic system in psychosis and predictions for the prodromal phase of psychosis.Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2007 Dec;51:s13-8. doi: 10.1192/bjp.191.51.s13. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2007. PMID: 18055930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Redefining the endophenotype concept to accommodate transdiagnostic vulnerabilities and etiological complexity.Biomark Med. 2017 Sep;11(9):769-780. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0002. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Biomark Med. 2017. PMID: 28891303 Free PMC article.
-
Brain neuroreceptor density and personality traits: towards dimensional biomarkers for psychiatric disorders.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 19;373(1744):20170156. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0156. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ventral striatal dopamine synthesis capacity is associated with individual differences in behavioral disinhibition.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Mar 14;8:86. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00086. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24672449 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia: an integrated sociodevelopmental-cognitive model.Lancet. 2014 May 10;383(9929):1677-1687. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62036-X. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24315522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internalizing-externalizing comorbidity and regional brain volumes in the ABCD study.Dev Psychopathol. 2021 Dec;33(5):1620-1633. doi: 10.1017/s0954579421000560. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Dev Psychopathol. 2021. PMID: 36238203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boileau I, Dagher A, Leyton M, Gunn RN, Baker GB, Diksic M, et al. Modeling sensitization to stimulants in humans: an [11C]raclopride/positron emission tomography study in healthy men. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1386–1395. - PubMed
-
- Caceres A, Hall DL, Zelaya FO, Williams SC, Mehta MA. Measuring fMRI reliability with the intra-class correlation coefficient. Neuroimage. 2009;45:758–768. - PubMed
-
- Cervenka S, Backman L, Cselenyi Z, Halldin C, Farde L. Associations between dopamine D2-receptor binding and cognitive performance indicate functional compartmentalization of the human striatum. Neuroimage. 2008;40:1287–1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

