IL-25 drives remodelling in allergic airways disease induced by house dust mite
- PMID: 23093652
- PMCID: PMC3534261
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202003
IL-25 drives remodelling in allergic airways disease induced by house dust mite
Abstract
Background: Overexpression of the transforming growth factor β family signalling molecule smad2 in the airway epithelium provokes enhanced allergen-induced airway remodelling in mice, concomitant with elevated levels of interleukin (IL)-25.
Objective: We investigated whether IL-25 plays an active role in driving this airway remodelling.
Methods: Anti-IL-25 antibody was given to mice exposed to either inhaled house dust mite (HDM) alone, or in conjunction with an adenoviral smad2 vector which promotes an enhanced remodelling phenotype.
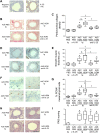
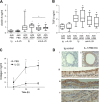
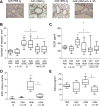
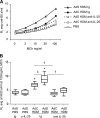
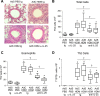
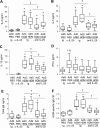
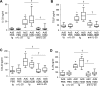
Results: Blocking IL-25 in allergen-exposed mice resulted in a moderate reduction in pulmonary eosinophilia and levels of T helper type 2 associated cytokines, IL-5 and IL-13. In addition, IL-25 neutralisation abrogated peribronchial collagen deposition, airway smooth muscle hyperplasia and airway hyperreactivity in control mice exposed to HDM and smad2-overexpressing mice. IL-25 was shown to act directly on human fibroblasts to induce collagen secretion. Recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells to the lung and subsequent neovascularisation was also IL-25 dependent, demonstrating a direct role for IL-25 during angiogenesis in vivo. Moreover, the secretion of innate epithelial derived cytokines IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) was completely ablated.
Conclusions: In addition to modulating acute inflammation, we now demonstrate a role for IL-25 in orchestrating airway remodelling. IL-25 also drives IL-33 and TSLP production in the lung. These data delineate a wider role for IL-25 in mediating structural changes to the lung following allergen exposure and implicate IL-25 as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of airway remodelling in asthma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Smad2 drives house dust mite-mediated airway remodeling and airway hyperresponsiveness via activin and IL-25.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Jul 15;182(2):143-54. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200905-0725OC. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20339149 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of TSLP inhibits airway remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma induced by chronic exposure to house dust mite.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e51268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051268. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23300949 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 promotes airway remodeling in pediatric patients with severe steroid-resistant asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Sep;132(3):676-685.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 Jun 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23759184 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and growth factors in airway remodeling in asthma.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):676-80. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.017. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17720466 Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus-Host Interactions Mediating Airway Wall Remodelling in Asthma.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;8(2):159. doi: 10.3390/jof8020159. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunologic aspects of asthma: from molecular mechanisms to disease pathophysiology and clinical translation.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 8;15:1478624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478624. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39439788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophil Lineage-Committed Progenitors as a Therapeutic Target for Asthma.Cells. 2021 Feb 16;10(2):412. doi: 10.3390/cells10020412. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33669458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absence of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 protects against house dust mite-induced pulmonary remodeling but not airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 May 1;306(9):L866-75. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00153.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24610935 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cells in the innate response to allergens and initiation of atopic asthma.J Clin Invest. 2018 Jul 2;128(7):3116-3128. doi: 10.1172/JCI97720. Epub 2018 Jun 18. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29911993 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct sustained structural and functional effects of interleukin-33 and interleukin-25 on the airways in a murine asthma surrogate.Immunology. 2015 Aug;145(4):508-18. doi: 10.1111/imm.12465. Epub 2015 May 17. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25807992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S, et al. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 2011;34:149–62 - PubMed
-
- Sharkhuu T, Matthaei KI, Forbes E, et al. Mechanism of interleukin-25 (IL-17E)-induced pulmonary inflammation and airways hyper-reactivity. Clin Exp Allergy 2006;36:1575–83 - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne SJ, Barlow JL, Jolin HE, et al. Blocking IL-25 prevents airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;120:1324–31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
