Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adult mice induces vision loss
- PMID: 23093773
- PMCID: PMC3484459
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI65157
Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adult mice induces vision loss
Abstract
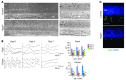
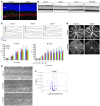
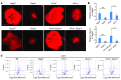
Current therapies directed at controlling vascular abnormalities in cancers and neovascular eye diseases target VEGF and can slow the progression of these diseases. While the critical role of VEGF in development has been well described, the function of locally synthesized VEGF in the adult eye is incompletely understood. Here, we show that conditionally knocking out Vegfa in adult mouse retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells, which regulate retinal homeostasis, rapidly leads to vision loss and ablation of the choriocapillaris, the major blood supply for the outer retina and photoreceptor cells. This deletion also caused rapid dysfunction of cone photoreceptors, the cells responsible for fine visual acuity and color vision. Furthermore, Vegfa deletion showed significant downregulation of multiple angiogenic genes in both physiological and pathological states, whereas the deletion of the upstream regulatory transcriptional factors HIFs did not affect the physiological expressions of angiogenic genes. These results suggest that endogenous VEGF provides critical trophic support necessary for retinal function. Targeting factors upstream of VEGF, such as HIFs, may be therapeutically advantageous compared with more potent and selective VEGF antagonists, which may have more off-target inhibitory trophic effects.
Figures
Comment in
-
Turning a blind eye to anti-VEGF toxicities.J Clin Invest. 2012 Nov;122(11):3849-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI65509. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23093785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dorrell MI, Aguilar E, Friedlander M. Retinal vascular development is mediated by endothelial filopodia, a preexisting astrocytic template and specific R-cadherin adhesion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43(11):3500–3510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

