Lung capillaries raise the hypoxia alarm
- PMID: 23093784
- PMCID: PMC3484463
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI65623
Lung capillaries raise the hypoxia alarm
Abstract
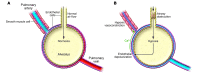
When ventilation is blocked, the lung can protect against the loss of blood oxygenation by activating localized arterial vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to underventilated regions, and redirecting flow to better-ventilated alveoli. This phenomenon, hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV), preserves the overall efficiency of blood oxygenation, but the mechanism by which the hypoxic signal is transmitted to the smooth muscle that contracts the arterioles has remained largely a mystery. In this issue of the JCI, Wang et al. reveal that the endothelial lining of the hypoxic alveoli plays a key role in sensing hypoxia and transmitting the signal to initiate HPV.
Figures
Comment on
-
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction requires connexin 40-mediated endothelial signal conduction.J Clin Invest. 2012 Nov;122(11):4218-30. doi: 10.1172/JCI59176. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23093775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conhaim RL, Staub NC. Reflection spectrophotometric measurement of O2 uptake in pulmonary arterioles of cats. J Appl Physiol. 1980;48(5):848–856. - PubMed

