Codon preference optimization increases prokaryotic cystatin C expression
- PMID: 23093857
- PMCID: PMC3471025
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/732017
Codon preference optimization increases prokaryotic cystatin C expression
Abstract
Gene expression is closely related to optimal vector-host system pairing in many prokaryotes. Redesign of the human cystatin C (cysC) gene using the preferred codons of the prokaryotic system may significantly increase cysC expression in Escherichia coli (E. coli). Specifically, cysC expression may be increased by removing unstable sequences and optimizing GC content. According to E. coli expression system codon preferences, the gene sequence was optimized while the amino acid sequence was maintained. The codon-optimized cysC (co-cysC) and wild-type cysC (wt-cysC) were expressed by cloning the genes into a pET-30a plasmid, thus transforming the recombinant plasmid into E. coli BL21. Before and after the optimization process, the prokaryotic expression vector and host bacteria were examined for protein expression and biological activation of CysC. The recombinant proteins in the lysate of the transformed bacteria were purified using Ni(2+)-NTA resin. Recombinant protein expression increased from 10% to 46% based on total protein expression after codon optimization. Recombinant CysC purity was above 95%. The significant increase in cysC expression in E. coli expression produced by codon optimization techniques may be applicable to commercial production systems.
Figures
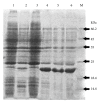
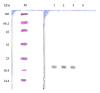
Similar articles
-
Effect of codon optimization on expression levels of human cystatin C in Pichia pastoris.Genet Mol Res. 2014 Jul 4;13(3):4990-5000. doi: 10.4238/2014.July.4.14. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 25062487
-
A purification method for tag-free human cystatin C recombinant protein expressed in Escherichia coli.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Feb 7;47(2):123-128. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2016.1181087. Epub 2016 May 4. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27143404
-
Expression and purification of soluble human cystatin C in Escherichia coli with maltose-binding protein as a soluble partner.Protein Expr Purif. 2014 Dec;104:14-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Protein Expr Purif. 2014. PMID: 25260712
-
Optimizing scaleup yield for protein production: Computationally Optimized DNA Assembly (CODA) and Translation Engineering.Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2007;13:27-42. doi: 10.1016/S1387-2656(07)13002-7. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2007. PMID: 17875472 Review.
-
[Effects of gene design on recombinant protein expression: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2013 Sep;29(9):1201-13. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 24409684 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Novel methods to optimize gene and statistic test for evaluation - an application for Escherichia coli.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Feb 10;18(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1517-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28187713 Free PMC article.
-
Codon optimisation is key for pernisine expression in Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 9;10(4):e0123288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123288. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25856104 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Expression and Catalytic Properties of Codon-Optimized Small-Sized Bromelain from MD2 Pineapple.Molecules. 2022 Sep 16;27(18):6031. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186031. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144767 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular immunity survey against urinary tract infection using pVAX/fimH cassette with mammalian and wild type codon usage as a DNA vaccine.Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2014 Jul;3(2):185-93. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2014.3.2.185. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2014. PMID: 25003092 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient expression of a cnidarian peptide-gated ion channel in mammalian cells.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):273-283. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1882762. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33522420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgess-Brown NA, Sharma S, Sobott F, Loenarz C, Oppermann U, Gileadi O. Codon optimization can improve expression of human genes in Escherichia coli: a multi-gene study. Protein Expression and Purification. 2008;59(1):94–102. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Z, Schnake P, Xiao L, Lal AA. Enhanced expression of a recombinant malaria candidate vaccine in Escherichia coli by codon optimization. Protein Expression and Purification. 2004;34(1):87–94. - PubMed
-
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1981;151(3):389–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

