Synthesis and kinetic evaluation of cyclophostin and cyclipostins phosphonate analogs as selective and potent inhibitors of microbial lipases
- PMID: 23095026
- PMCID: PMC3518039
- DOI: 10.1021/jm301216x
Synthesis and kinetic evaluation of cyclophostin and cyclipostins phosphonate analogs as selective and potent inhibitors of microbial lipases
Abstract
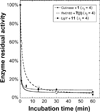
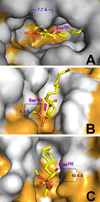
A new series of customizable diastereomeric cis- and trans-monocyclic enol-phosphonate analogs to Cyclophostin and Cyclipostins were synthesized. Their potencies and mechanisms of inhibition toward six representative lipolytic enzymes belonging to distinct lipase families were examined. With mammalian gastric and pancreatic lipases no inhibition occurred with any of the compounds tested. Conversely, Fusarium solani Cutinase and lipases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Rv0183 and LipY) were all fully inactivated. The best inhibitors displayed a cis conformation (H and OMe) and exhibited higher inhibitory activities than the lipase inhibitor Orlistat toward the same enzymes. Our results have revealed that chemical group at the γ-carbon of the phosphonate ring strongly impacts the inhibitory efficiency, leading to a significant improvement in selectivity toward a target lipase over another. The powerful and selective inhibition of microbial (fungal and mycobacterial) lipases suggests that these seven-membered monocyclic enol-phosphonates should provide useful leads for the development of novel and highly selective antimicrobial agents.
Figures
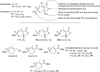

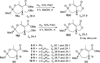
References
-
- Schmid RD, Verger R. Lipases: interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998;37:1608–1633. - PubMed
-
- Vulfson E. Lipases: Their Structure, Biochemistry, and Application. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1994. Industrial applications of lipases; pp. 271–288.
-
- Lengsfeld H, Beaumier-Gallon G, Chahinian H, De Caro A, Verger R, Laugier R, Carrière F. Physiology of Gastrointestinal Lipolysis and Therapeutical Use of Lipases and Digestive Lipase Inhibitors. In: Müller G, Petry S, editors. Lipases and phospholipases in drug development. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2004. pp. 195–223.
-
- Hadvàry P, Sidler W, Meister W, Vetter W, Wolfer H. The lipase inhibitor tetrahydrolipstatin binds covalently to the putative active site serine of pancreatic lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:2021–2027. - PubMed
-
- Carrière F, Renou C, Ransac S, Lopez V, De Caro J, Ferrato F, De Caro A, Fleury A, Sanwald-Ducray P, Lengsfeld H, Beglinger C, Hadvary P, Verger R, Laugier R. Inhibition of gastrointestinal lipolysis by Orlistat during digestion of test meals in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G16–G28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

