Improved awareness and appropriate use of non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (nPEP) for HIV prevention following a multi-modal communication strategy
- PMID: 23095456
- PMCID: PMC3503851
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-906
Improved awareness and appropriate use of non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (nPEP) for HIV prevention following a multi-modal communication strategy
Abstract
Background: In May 2005, the Western Australian Department of Health (WA Health) developed a communication strategy to improve the awareness and appropriate use of non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (nPEP) in WA. The communication strategy included the development of an nPEP information pamphlet, the establishment of a 24 hour nPEP phone line and the distribution of the WA Health nPEP guidelines to health professionals. The communication strategy was aimed at gay men, people in sero-discordant relationships, people living with HIV, injecting drug users and health care providers with patients from these populations. This evaluation aimed to assess the awareness and appropriate use of nPEP in WA before and after the commencement of the nPEP communication strategy.
Methods: A program logic method was used to identify the immediate (short-term) and ultimate (long-term) outcomes of the communication strategy. The achievement of these outcomes was evaluated using data from website statistics, a survey of 'sexuality sensitive' doctors, statistics published in Perth Gay Community Periodic Surveys (PGCPS) and data from the WA nPEP database. A χ(2) test for trend was conducted to identify any significant changes in the ultimate outcome indicators pre- and post-strategy.
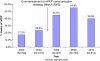
Results: nPEP awareness among gay men in the PGCPS initially increased from 17.2% in 2002 to 54.9% in 2008, then decreased to 39.9% in 2010. After the commencement of the communication strategy, the proportion of nPEP prescriptions meeting the eligibility criteria for nPEP significantly increased (61.2% in 2002-2005 to 90.0% in 2008-2010 (p < .001)). The proportion of nPEP recipients who completed the prescribed course of nPEP (46.6% in 2002-2005 to 66.9% in 2008-2010 (p = .003)) and the proportion who received a post-nPEP HIV test three to four months after the first visit for nPEP (38.8% in 2002-2005 to 51.9% in 2008-2010 (p = .023)) also increased.
Conclusions: Since the introduction of the nPEP communication strategy, the delivery and appropriate use of nPEP have significantly improved in WA. In the 2008-2010 period, an improvement in HIV testing of nPEP recipients at three month follow-up was reported for the first time in WA. However, there is a need for ongoing activities to raise nPEP awareness among gay men.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after Non-occupational exposure to HIV. http://www.ashm.org.au/images/publications/guidelines/2007nationalnpepgu....
-
- Hull P, Brown G, Rawstorne P, Prestage G, Kippax S, Langdon T. Gay community periodic survey. Perth; 2004. http://nchsr.arts.unsw.edu.au/media/File/Perth_GCPS_2004.pdf.
-
- Rogers PJ. Using programme theory to evaluate complicated and complex aspects of interventions. Evaluation. 2008;14(1):29–48. doi: 10.1177/1356389007084674. - DOI
-
- Hull P, Brown G, van de Ven P, Prestage G, Rawstorne P, Kippax S, Langdon T. Gay community periodic survey. Perth; 2002. http://nchsr.arts.unsw.edu.au/media/File/Perth_GCPS__2002.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical