High-Throughput parallel blind Virtual Screening using BINDSURF
- PMID: 23095663
- PMCID: PMC3504923
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S14-S13
High-Throughput parallel blind Virtual Screening using BINDSURF
Abstract
Background: Virtual Screening (VS) methods can considerably aid clinical research, predicting how ligands interact with drug targets. Most VS methods suppose a unique binding site for the target, usually derived from the interpretation of the protein crystal structure. However, it has been demonstrated that in many cases, diverse ligands interact with unrelated parts of the target and many VS methods do not take into account this relevant fact.
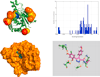
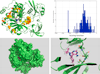
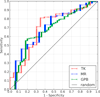
Results: We present BINDSURF, a novel VS methodology that scans the whole protein surface in order to find new hotspots, where ligands might potentially interact with, and which is implemented in last generation massively parallel GPU hardware, allowing fast processing of large ligand databases.
Conclusions: BINDSURF is an efficient and fast blind methodology for the determination of protein binding sites depending on the ligand, that uses the massively parallel architecture of GPUs for fast pre-screening of large ligand databases. Its results can also guide posterior application of more detailed VS methods in concrete binding sites of proteins, and its utilization can aid in drug discovery, design, repurposing and therefore help considerably in clinical research.
Figures






References
-
- Garland M, Kirk DB. Understanding throughput-oriented architectures. Commun ACM. 2010;53:58–66.
-
- Garland M, Le Grand S, Nickolls J, Anderson J, Hardwick J, Morton S, Phillips E, Zhang Y, Volkov V. Parallel Computing Experiences with CUDA. IEEE Micro. 2008;28:13–27.
-
- NVIDIA. Whitepaper NVIDIA's Next Generation CUDA Compute Architecture: Fermi. 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

