Chemical synthesis, backbone cyclization and oxidative folding of cystine-knot peptides: promising scaffolds for applications in drug design
- PMID: 23095896
- PMCID: PMC6268209
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules171112533
Chemical synthesis, backbone cyclization and oxidative folding of cystine-knot peptides: promising scaffolds for applications in drug design
Abstract
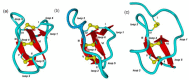
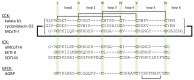
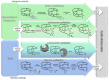
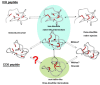
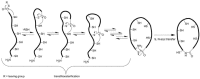
Cystine-knot peptides display exceptional structural, thermal, and biological stability. Their eponymous motif consists of six cysteine residues that form three disulfide bonds, resulting in a notably rigid structural core. Since they highly tolerate either rational or combinatorial changes in their primary structure, cystine knots are considered to be promising frameworks for the development of peptide-based pharmaceuticals. Despite their relatively small size (two to three dozens amino acid residues), the chemical synthesis route is challenging since it involves critical steps such as head-to-tail cyclization and oxidative folding towards the respective bioactive isomer. Herein we describe the topology of cystine-knot peptides, their synthetic availability and briefly discuss potential applications of engineered variants in diagnostics and therapy.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

