Propranolol accelerates adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells and causes apoptosis of hemangioma endothelial cells
- PMID: 23096601
- PMCID: PMC3668332
- DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318267d3db
Propranolol accelerates adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells and causes apoptosis of hemangioma endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Infantile hemangiomas can cause significant morbidity during proliferation, yet there is no U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved treatment. They are believed to form from hemangioma stem cells, which differentiate toward a hemangioma endothelial cell phenotype. Recently, propranolol has demonstrated effectiveness in treating complicated infantile hemangiomas. The authors hypothesize that propranolol facilitates their involution by altering cellular behavior in both hemangioma endothelial and stem cells.
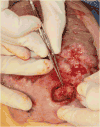
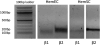
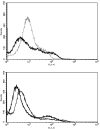
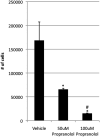
Methods: Hemangioma endothelial and stem cells were isolated from resected infantile hemangioma specimens. Cells were treated with 100 μM propranolol for 48 hours, and apoptosis was determined by the presence of annexin V antibody. Proliferation of stem and endothelial cells was assessed after treatment with 50 or 100 μM propranolol or vehicle, for 72 and 96 hours, respectively. Adipogenesis was induced in stem cells with and without propranolol. Pro-adipogenic genes PPARδ, PPARγ, C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, RXRα, and RXRγ were analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
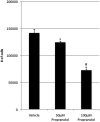
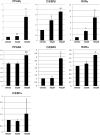
Results: Annexin V levels were increased in propranolol-treated endothelial cells but not in stem cells. Proliferation of stem and endothelial cells was inhibited by propranolol in a dose-dependent manner. Propranolol-treated stem cells demonstrated accelerated adipogenesis when compared with untreated controls. Transcript levels of C/EBPβ (p < 0.05), RXRγ (p < 0.05), and PPARγ (p < 0.02) were significantly increased when treated with 50 or 100 μM propranolol; and C/EBPδ (p < 0.05), RXRα (p < 0.05), and PPARδ (p < 0.01) transcripts were increased when treated with 100 μM propranolol. C/EBPα transcript levels remained unchanged at either dose.
Conclusions: Propranolol increased apoptosis of hemangioma endothelial cells, but not stem cells, and accelerated adipogenesis of hemangioma stem cells. Thus, propranolol likely accelerates involution to fibrofatty residuum.
Figures

References
-
- Frieden IJ, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, et al. Infantile hemangiomas: current knowledge, future directions. Proceedings of a research workshop on infantile hemangiomas, April 7-9, 2005, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:383–406. - PubMed
-
- Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E, et al. Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas: clinical characteristics predicting complications and treatment. Pediatrics. 2006;118:882–887. - PubMed
-
- Chamlin SL, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, et al. Multicenter prospective study of ulcerated hemangiomas. J Pediatr. 2007;151:684–689. 689 e681. - PubMed
-
- Boon LM, Burrows PE, Paltiel HJ, et al. Hepatic vascular anomalies in infancy: a twenty-seven-year experience. J Pediatr. 1996;129:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Arneja JS, Mulliken JB. Resection of amblyogenic periocular hemangiomas: indications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:274–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

