Primary culture of mammalian taste epithelium
- PMID: 23097103
- PMCID: PMC3638988
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-125-7_7
Primary culture of mammalian taste epithelium
Abstract
Establishment of primary and immortalized cultures of many cell types has facilitated efforts to understand the signals involved in proliferation and differentiation and yielded tools to rapidly assay new molecules targeting specific receptor pathways. Taste cells are specialized sensory epithelial cells which reside within taste buds on the lingual epithelium. Only recently have successful culturing protocols been developed which maintain essential molecular and functional characteristics. These protocols provide a tractable tool to examine the molecular, regenerative, and functional properties of these unique sensory cells within a controlled environment. The method involves an enzymatic isolation procedure and standardized culture conditions, and may be applied to either dissected rodent tissue or human fungiform papillae obtained by biopsy. Human fungiform cells can be maintained in culture for more than seven passages, without loss of viability and with retention of the molecular and biochemical properties of acutely isolated taste cells. Cultured primary human fungiform papillae cells also exhibit functional responses to taste stimuli indicating the presence of taste receptors and at least some relevant signaling pathways. While the loss of the three-dimensional structure of the intact taste bud must be taken into consideration in interpreting results obtained with these cells, this culture protocol provides a useful model for molecular studies of the proliferation, differentiation, and physiological function of mammalian taste receptor cells.
Figures


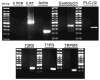
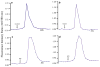
References
-
- Arvidson K. Location and variation in number of taste buds in human fungiform papillae. Scand J Dent Res. 1979;87:435–442. - PubMed
-
- Barlow LA, Northcutt RG. Analysis of the embryonic lineage of vertebrate taste buds. Chem Senses. 1994;19:715–724. - PubMed
-
- Bezencon C, Le Coutre J, Damak S. Taste-signaling proteins are coexpressed in solitary intestinal epithelial cells. Chem Senses. 2007;32:41–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

