RNA-ID, a highly sensitive and robust method to identify cis-regulatory sequences using superfolder GFP and a fluorescence-based assay
- PMID: 23097427
- PMCID: PMC3504683
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.035907.112
RNA-ID, a highly sensitive and robust method to identify cis-regulatory sequences using superfolder GFP and a fluorescence-based assay
Abstract
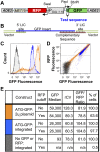
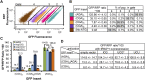
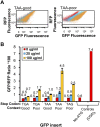
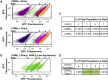
We have developed a robust and sensitive method, called RNA-ID, to screen for cis-regulatory sequences in RNA using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of yeast cells bearing a reporter in which expression of both superfolder green fluorescent protein (GFP) and yeast codon-optimized mCherry red fluorescent protein (RFP) is driven by the bidirectional GAL1,10 promoter. This method recapitulates previously reported progressive inhibition of translation mediated by increasing numbers of CGA codon pairs, and restoration of expression by introduction of a tRNA with an anticodon that base pairs exactly with the CGA codon. This method also reproduces effects of paromomycin and context on stop codon read-through. Five key features of this method contribute to its effectiveness as a selection for regulatory sequences: The system exhibits greater than a 250-fold dynamic range, a quantitative and dose-dependent response to known inhibitory sequences, exquisite resolution that allows nearly complete physical separation of distinct populations, and a reproducible signal between different cells transformed with the identical reporter, all of which are coupled with simple methods involving ligation-independent cloning, to create large libraries. Moreover, we provide evidence that there are sequences within a 9-nt library that cause reduced GFP fluorescence, suggesting that there are novel cis-regulatory sequences to be found even in this short sequence space. This method is widely applicable to the study of both RNA-mediated and codon-mediated effects on expression.
Figures
References
-
- Alexandrov A, Vignali M, LaCount DJ, Quartley E, de Vries C, De Rosa D, Babulski J, Mitchell SF, Schoenfeld LW, Fields S, et al. 2004. A facile method for high-throughput co-expression of protein pairs. Mol Cell Proteomics 3: 934–938 - PubMed
-
- Barrera LO, Ren B 2006. The transcriptional regulatory code of eukaryotic cells—insights from genome-wide analysis of chromatin organization and transcription factor binding. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 291–298 - PubMed
-
- Bonetti B, Fu L, Moon J, Bedwell DM 1995. The efficiency of translation termination is determined by a synergistic interplay between upstream and downstream sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol 251: 334–345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
