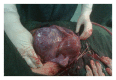
Placenta percreta invading broad ligament and parametrium in a woman with two previous cesarean sections: a case report
- PMID: 23097727
- PMCID: PMC3477658
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/251381
Placenta percreta invading broad ligament and parametrium in a woman with two previous cesarean sections: a case report
Abstract
Introduction. The incidence of placenta accreta has dramatically increased due to increasing caesarean section rate all over the world. Placenta percreta is the most severe form of placenta accretes. It frequently results in maternal morbidity and mortality mainly caused by massive obstetric hemorrhage or emergency hysterectomy. Percreta invading into the broad ligament has rarely been previously reported. Case presenting. We presented a case of placenta percreta invading left broad ligament and parametrium in a woman with two previous cesarean sections, which led to massive intraoperative hemorrhage during hysterectomy and transient ischemic encephalopathy. Conclusion. In cases of parametrial involvement, it would be more difficult to decide whether to remove placenta or leave it in site. In surgical removal neither local excision of placental bed and uterine repair nor traditional hysterectomy is adequate if parametrium invaded by placenta. We suggest delayed elective hysterectomy in such cases. So, pregnancy-induced pelvic congestion would be decreased, we can gather an expert team of gynecologists, urologists, and vascular surgeons, we could get plenty of blood products, and we may have the chance to administer methotrexate.
Figures
References
-
- O’Brien JM, Barton JR, Donaldson ES. The management of placenta percreta: conservative and operative strategies. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1996;175(6):1632–1638. - PubMed
-
- Honig A, Rieger L, Thanner F, Eck M, Sutterlin M, Dietl J. Placenta percreta with subsequent uterine rupture at 15 weeks of gestation after two previous cesarean sections. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 2005;31(5):439–443. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Kocherginsky M, Hibbard JU. Abnormal placentation: twenty-year analysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2005;192(5):1458–1461. - PubMed
-
- Seoud M, Cheaib S, Birjawi G, Tawil A, Jamali F. Successful treatment of severe retro-peritoneal bleeding with recombinant factor VIIa in women with placenta percreta invading into the left broad ligament: unusual repeated ante-partum intra-abdominal bleeding. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 2010;36(1):183–186. - PubMed
-
- Lin CC, Adamczyk CJ, Montag AG, Zelop CM, Snow JC. Placenta previa percreta involving the left broad ligament and cervix: a case report. Journal of Reproductive Medicine for the Obstetrician and Gynecologist. 1998;43(9):839–843. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources