Human Organic Solute Transporter (hOST): protein interaction and membrane sorting process
- PMID: 23097745
- PMCID: PMC3476788
Human Organic Solute Transporter (hOST): protein interaction and membrane sorting process
Abstract
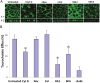
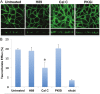
The human organic solute transporter (hOST) is a heterodimer composed of alpha and beta subunits. Physical association of hOSTα and β subunits is essential for their polarized basolateral plasma membrane localization and function in the export of bile acids and steroids. To understand the role of carboxyl- and amino-tails of OSTβ and mechanisms underlying membrane localization of hOST, the effects of tail deletion of the hOSTβ subunit and biological reagents on membrane distribution and transport function of hOST were investigated in stably transfected MDCK cells. After deletion of 35 amino acids from the amino-tail of hOSTβ, the efflux transport activity and polarized membrane distribution of the truncated hOSTβ was abolished. A co-immunoprecipitation study verified that the amino-tail of hOSTβ is essential for the association with hOSTα subunit. Treatments with acytochalasin D (interrupting ctin-filaments), bafilomycin A1 (inhibiting vacuolar H(+)-ATPase), brefeldin A (disrupting the Golgi complex), and calphostin C (inhibiting protein kinase C), significantly disrupted the polarized membrane distribution of hOST and markedly reduced transport activity in stably transfected MDCK cells. In summary, the 35 amino acid amino-terminal fragment of hOSTβ contains critical information for interaction with the hOSTα subunit and subsequent trafficking to the plasma membrane. These studies suggest that the membrane sorting process of hOST is mediated by a bafilomycin A1-sensitive vesicular pathway that is associated with the actin-cytoskeleton network. The membrane localization of hOST is also partially mediated through a brefeldin A sensitive mechanism, which controls its transit from the ER to Golgi and is regulated by PKC.
Keywords: Human OST; membrane trafficking; organic anion transporter; protein interaction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Novel Di-Leucine Motif at the N-Terminus of Human Organic Solute Transporter Beta Is Essential for Protein Association and Membrane Localization.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 28;11(6):e0158269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158269. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27351185 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane trafficking of the human organic anion-transporting polypeptide C (hOATPC).Pharm Res. 2008 Feb;25(2):463-74. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9399-9. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17641954
-
Protein-protein interactions and membrane localization of the human organic solute transporter.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):G1586-93. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00457.2006. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17332473
-
Biology of a novel organic solute and steroid transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005 Nov;230(10):689-98. doi: 10.1177/153537020523001001. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005. PMID: 16246895 Review.
-
The heteromeric organic solute transporter, OSTα-OSTβ/SLC51: a transporter for steroid-derived molecules.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):683-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.11.005. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23506901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Di-Leucine Motif at the N-Terminus of Human Organic Solute Transporter Beta Is Essential for Protein Association and Membrane Localization.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 28;11(6):e0158269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158269. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27351185 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Absorption of Bile Acids in Health and Disease.Compr Physiol. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):21-56. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190007. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31853951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights into the organic solute transporter alpha/beta, OSTα/β: From the bench to the bedside.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Jul;211:107542. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107542. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32247663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral delivery of proteins and peptides: Challenges, status quo and future perspectives.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Aug;11(8):2416-2448. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34522593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seward DJ, Koh AS, Boyer JL, Ballatori N. Functional complementation between a novel mammalian polygenic transport complex and an evolutionarily ancient organic solute transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27473–82. - PubMed
-
- Ballatori N, Christian WV, Lee JY, Dawson PA, Soroka CJ, Boyer JL, Madejczyk MS, Li N. OSTalpha-OSTbeta: a major basolateral bile acid and steroid transporter in human intestinal, renal, and biliary epithelia. Hepatology. 2005;42:1270–9. - PubMed
-
- Boyer JL, Trauner M, Mennone A, Soroka CJ, Cai SY, Moustafa T, Zollner G, Lee JY, Ballatori N. Upregulation of a basolateral FXR-dependent bile acid efflux transporter OSTalpha-OSTbeta in cholestasis in humans and rodents. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G1124–30. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
