AKAP150-anchored calcineurin regulates synaptic plasticity by limiting synaptic incorporation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors
- PMID: 23100425
- PMCID: PMC3504485
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3326-12.2012
AKAP150-anchored calcineurin regulates synaptic plasticity by limiting synaptic incorporation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors
Abstract
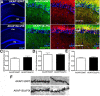
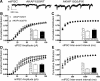
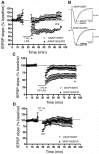
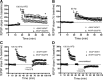
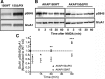
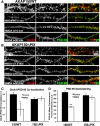
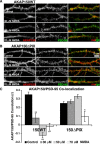
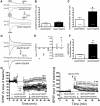
AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are tetrameric ion channels assembled from GluA1-GluA4 subunits that mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. In the hippocampus, most synaptic AMPARs are composed of GluA1/2 or GluA2/3 with the GluA2 subunit preventing Ca(2+) influx. However, a small number of Ca(2+)-permeable GluA1 homomeric receptors reside in extrasynaptic locations where they can be rapidly recruited to synapses during synaptic plasticity. Phosphorylation of GluA1 S845 by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) primes extrasynaptic receptors for synaptic insertion in response to NMDA receptor Ca(2+) signaling during long-term potentiation (LTP), while phosphatases dephosphorylate S845 and remove synaptic and extrasynaptic GluA1 during long-term depression (LTD). PKA and the Ca(2+)-activated phosphatase calcineurin (CaN) are targeted to GluA1 through binding to A-kinase anchoring protein 150 (AKAP150) in a complex with PSD-95, but we do not understand how the opposing activities of these enzymes are balanced to control plasticity. Here, we generated AKAP150ΔPIX knock-in mice to selectively disrupt CaN anchoring in vivo. We found that AKAP150ΔPIX mice lack LTD but express enhanced LTP at CA1 synapses. Accordingly, basal GluA1 S845 phosphorylation is elevated in AKAP150ΔPIX hippocampus, and LTD-induced dephosphorylation and removal of GluA1, AKAP150, and PSD-95 from synapses are impaired. In addition, basal synaptic activity of GluA2-lacking AMPARs is increased in AKAP150ΔPIX mice and pharmacologic antagonism of these receptors restores normal LTD and inhibits the enhanced LTP. Thus, AKAP150-anchored CaN opposes PKA phosphorylation of GluA1 to restrict synaptic incorporation of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPARs both basally and during LTP and LTD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 14;38(11):2863-2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29440558 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptor-Dependent LTD Requires Transient Synaptic Incorporation of Ca²⁺-Permeable AMPARs Mediated by AKAP150-Anchored PKA and Calcineurin.Neuron. 2016 Mar 2;89(5):1000-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.043. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26938443 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid disruption of LTP/LTD balance is mediated by AKAP150-anchored PKA and Calcineurin regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 5;37(1):109786. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109786. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34610314 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
How Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors, the kinase PKA, and the phosphatase PP2B are intertwined in synaptic LTP and LTD.Sci Signal. 2016 Apr 26;9(425):e2. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf7067. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27117250 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Phosphatase 2B Dual Function Facilitates Synaptic Integrity and Motor Learning.J Neurosci. 2021 Jun 30;41(26):5579-5594. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1741-20.2021. Epub 2021 May 21. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34021041 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Single Head Exposure to GSM-1800 MHz Signals on the Transcriptome Profile in the Rat Cerebral Cortex: Enhanced Gene Responses Under Proinflammatory Conditions.Neurotox Res. 2020 Jun;38(1):105-123. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00191-3. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 32200527 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol prevents electroconvulsive-shock-induced memory impairment through regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity in a rat model of depression.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Sep 23;10:1847-59. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S67108. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 25285008 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic strategies for anchored kinases and phosphatases: exploiting short linear motifs and intrinsic disorder.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Jul 28;6:158. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00158. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26283967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction and Subcellular Association of PRRT1/SynDIG4 With AMPA Receptors.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021 Aug 2;13:705664. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.705664. eCollection 2021. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34408636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, Yasuda H, von Zastrow M, Malenka RC. Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1291–1300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
