Immune complexes isolated from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis modulate the activation and function of normal granulocytes
- PMID: 23100480
- PMCID: PMC3535873
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00437-12
Immune complexes isolated from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis modulate the activation and function of normal granulocytes
Abstract
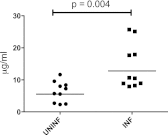
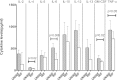
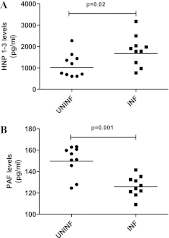
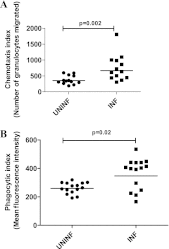
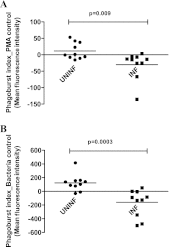
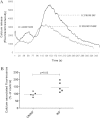
Circulating immune complexes (ICs) are associated with the pathogenesis of several diseases. Very little is known about the effect of ICs on the host immune response in patients with tuberculosis (TB). The effects of ICs isolated from patients with TB in modulating the release of calcium, cytokines, and granular proteins were studied in normal granulocytes, as were their chemotactic, phagocytic, and oxidative burst processes. ICs from TB patients induced decreased production of cytokines and platelet-activating factor (PAF) from normal granulocytes. ICs from TB patients also induced enhanced chemotaxis and phagocytosis but caused diminished oxidative burst. This was accompanied by an increased release in intracellular calcium. On the other hand, ICs from TB patients induced increased release of the granular proteins human neutrophil peptides 1 to 3 (HNP1-3). Thus, ICs from patients with TB exhibit a profound effect on granulocyte function with activation of certain effector mechanisms and dampening of others.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chelation of Free Zn²⁺ Impairs Chemotaxis, Phagocytosis, Oxidative Burst, Degranulation, and Cytokine Production by Neutrophil Granulocytes.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 May;171(1):79-88. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0515-0. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26400651
-
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), LPS-immune complexes and cytokines as inducers of pulmonary inflammation in patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection.APMIS Suppl. 1995;50:1-30. APMIS Suppl. 1995. PMID: 7756034
-
Depressed phagocytosis and oxidative burst in polymorphonuclear leukocytes from individuals with pulmonary tuberculosis with or without human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998 Jan;5(1):41-4. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.5.1.41-44.1998. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9455878 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders of phagocyte function: biochemical aspects.Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977;13:157-69. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977. PMID: 45476 Review.
-
Inhaled Corticosteroids And Risk Of Tuberculosis In Patients With Obstructive Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis Of Non-randomized Studies.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Sep 26;14:2219-2227. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S209273. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019. PMID: 31576118 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High occurrence of simultaneous multiple-drug hypersensitivity syndrome induced by first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs.World Allergy Organ J. 2021 Jul 28;14(7):100562. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2021.100562. eCollection 2021 Jul. World Allergy Organ J. 2021. PMID: 34386151 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoproteins in circulating immune complexes are biomarkers of patients with Indian PKDL: A study from endemic districts of West Bengal, India.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 8;13(2):e0192302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192302. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29420575 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophil Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes in TB: What We Know so Far.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 14;10:2639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02639. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31798582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Leishmania donovani antigen in circulating immune complexes of visceral leishmaniasis subjects for diagnosis.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 18;12(8):e0182474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182474. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28820895 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Cell Wall Antigens Induce the Formation of Immune Complexes and the Development of Vasculitis in an Experimental Murine Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 8;24(2):1242. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021242. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernardo J, Hartlaub H, Yu X, Long H, Simons ER. 2002. Immune complex stimulation of human neutrophils involves a novel Ca2+/H+ exchanger that participates in the regulation of cytoplasmic pH: flow cytometric analysis of Ca2+/pH responses by subpopulations. J. Leukoc. Biol. 72:1172–1179 - PubMed
-
- Böyum A. 1968. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. Suppl. 97:77–89 - PubMed
-
- Burgos RA, Conejeros I, Hidalgo MA, Werling D, Hermosilla C. 2011. Calcium influx, a new potential therapeutic target in the control of neutrophil-dependent inflammatory diseases in bovines. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 143:1–10 - PubMed
-
- Cochrane CG. 1977. Role of granulocytes in immune complex-induced tissue injuries. Inflammation 2:319–333 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

