Therapeutic opportunities for targeting the ubiquitous cell surface receptor CD47
- PMID: 23101472
- PMCID: PMC3564224
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.2013.733699
Therapeutic opportunities for targeting the ubiquitous cell surface receptor CD47
Abstract
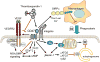
Introduction: CD47 is a ubiquitously expressed cell surface receptor that serves as a counter-receptor for SIRPα in recognition of self by the innate immune system. Independently, CD47 also functions as an important signaling receptor for regulating cell responses to stress.
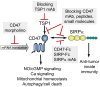
Areas covered: We review the expression, molecular interactions, and pathophysiological functions of CD47 in the cardiovascular and immune systems. CD47 was first identified as a potential tumor marker, and we examine recent evidence that its dysregulation contributes to cancer progression and evasion of anti-tumor immunity. We further discuss therapeutic strategies for enhancing or inhibiting CD47 signaling and applications of such agents in preclinical models of ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injuries, organ transplantation, pulmonary hypertension, radioprotection, and cancer.
Expert opinion: Ongoing studies are revealing a central role of CD47 for conveying signals from the extracellular microenvironment that limit cell and tissue survival upon exposure to various types of stress. Based on this key function, therapeutics targeting CD47 or its ligands thrombospondin-1 and SIRPα could have broad applications spanning reconstructive surgery, engineering of tissues and biocompatible surfaces, vascular diseases, diabetes, organ transplantation, radiation injuries, inflammatory diseases, and cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH/NCI (D.D.R.), by a NCI Director’s Career Development Innovation Award (D.R.S-P), by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (R01HL108954 2, R01HL089658, 1P01HL103455 to J.S.I.), the American Heart Association (11BGIA7210001 to J.S.I.), the Institute for Transfusion Medicine and the Hemophilia Center of Western Pennsylvania (to J.S.I.), and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (APP1016276 C.J. Martin Award to N.M.R.).
Figures

References
-
- Frazier WA, Isenberg JS, Kaur S, et al. CD47. UCSD Nature Molecule. 2010 doi: 10.1038/mp.a002870.01. - DOI
-
- Lindberg FP, Lublin DM, Telen MJ, et al. Rh-related antigen CD47 is the signal-transducer integrin-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:1567–70. - PubMed
-
- Poels LG, Peters D, van Megen Y, et al. Monoclonal antibody against human ovarian tumor-associated antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986;76:781–91. First identification of CD47 over-expression in cancer. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
