Single-neuron sequencing analysis of L1 retrotransposition and somatic mutation in the human brain
- PMID: 23101622
- PMCID: PMC3567441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.09.035
Single-neuron sequencing analysis of L1 retrotransposition and somatic mutation in the human brain
Abstract
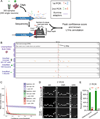
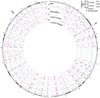
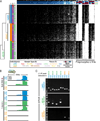
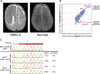
A major unanswered question in neuroscience is whether there exists genomic variability between individual neurons of the brain, contributing to functional diversity or to an unexplained burden of neurological disease. To address this question, we developed a method to amplify genomes of single neurons from human brains. Because recent reports suggest frequent LINE-1 (L1) retrotransposition in human brains, we performed genome-wide L1 insertion profiling of 300 single neurons from cerebral cortex and caudate nucleus of three normal individuals, recovering >80% of germline insertions from single neurons. While we find somatic L1 insertions, we estimate <0.6 unique somatic insertions per neuron, and most neurons lack detectable somatic insertions, suggesting that L1 is not a major generator of neuronal diversity in cortex and caudate. We then genotyped single cortical cells to characterize the mosaicism of a somatic AKT3 mutation identified in a child with hemimegalencephaly. Single-neuron sequencing allows systematic assessment of genomic diversity in the human brain.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

