Baeyer-Villiger C-C bond cleavage reaction in gilvocarcin and jadomycin biosynthesis
- PMID: 23102024
- PMCID: PMC3498853
- DOI: 10.1021/ja3081154
Baeyer-Villiger C-C bond cleavage reaction in gilvocarcin and jadomycin biosynthesis
Abstract
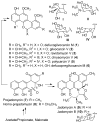
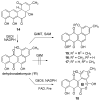
GilOII has been unambiguously identified as the key enzyme performing the crucial C-C bond cleavage reaction responsible for the unique rearrangement of a benz[a]anthracene skeleton to the benzo[d]naphthopyranone backbone typical of the gilvocarcin-type natural anticancer antibiotics. Further investigations of this enzyme led to the isolation of a hydroxyoxepinone intermediate, leading to important conclusions regarding the cleavage mechanism.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

