Validity of perceived weight gain in women using long-acting reversible contraception and depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
- PMID: 23103344
- PMCID: PMC3974101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.10.876
Validity of perceived weight gain in women using long-acting reversible contraception and depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
Abstract
Objective: The objective of the study was to evaluate perceived weight gain in women using contraception and determine the validity of self-reported weight gain.
Study design: We analyzed data from new contraceptive method users who self-reported a weight change at 3, 6, and 12 months after enrollment. We examined a subgroup of participants with objective weight measurements at baseline and 12 months to test the validity of self-reported weight gain.
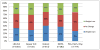
Results: Thirty-four percent of participants (1407 of 4133) perceived weight gain. Compared with copper intrauterine device users, implant users (relative risk, 1.29; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.51) and depot medroxyprogesterone acetate users (relative risk, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.64) were more likely to report perceived weight gain. Women who perceived weight gain experienced a mean weight gain of 10.3 pounds. The sensitivity and specificity of perceived weight gain were 74.6% and 84.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: In most women, perceived weight gain represents true weight gain. Implant and depot medroxyprogesterone acetate users are more likely to perceive weight gain among contraception users.
Copyright © 2013 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bahamondes L, Pinho F, de Melo NR, Oliveira E, Bahamondes MV. Associated factors with discontinuation use of combined oral contraceptives. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 33:303–9. - PubMed
-
- Hani D, Imthurn B, Merki-Feld GS. Weight gain due to hormonal contraception: myth or truth? Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch. 2009;49:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Bonny AE, Ziegler J, Harvey R, Debanne SM, Secic M, Cromer BA. Weight gain in obese and nonobese adolescent girls initiating depot medroxyprogesterone, oral contraceptive pills, or no hormonal contraceptive method. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160:40–5. - PubMed
-
- Pantoja M, Medeiros T, Baccarin MC, Morais SS, Bahamondes L, Fernandes AM. Variations in body mass index of users of depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate as a contraceptive. Contraception. 81:107–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical