Population pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in Chinese children with epilepsy
- PMID: 23103620
- PMCID: PMC4011358
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.118
Population pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in Chinese children with epilepsy
Abstract
Aim: To establish a population pharmacokinetics (PPK) model for lamotrigine (LTG) in Chinese children with epilepsy in order to formulate an individualized dosage guideline.
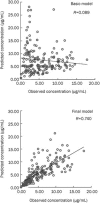
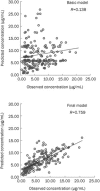
Methods: LTG steady-state plasma concentration data from therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) were collected retrospectively from 284 patients, with a total of 404 plasma drug concentrations. LTG concentrations were determined using a HPLC method. The patients were divided into 2 groups: PPK model group (n=116) and PPK valid group (n=168). A PPK model of LTG was established with NONMEM based on the data from PPK model group according to a one-compartment model with first order absorption and elimination. To validate the basic and final model, the plasma drug concentrations of the patients in PPK model group and PPK valid group were predicted by the two models.
Results: The final regression model for LTG was as follows: CL (L/h)=1.01*(TBW/27.87)(0.635)*e(-0.753*VPA)*e(0.868*CBZ)*e(0.633*PB), Vd (L)= 16.7*(TBW/27.87). The final PPK model was demonstrated to be stable and effective in the prediction of serum LTG concentrations by an internal and external approach validation.
Conclusion: A PPK model of LTG in Chinese children with epilepsy was successfully established with NONMEM. LTG concentrations can be predicted accurately by this model. The model may be very useful for establishing initial LTG dosage guidelines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine co-administered with valproic acid in Chinese epileptic children using nonlinear mixed effects modeling.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 May;74(5):583-591. doi: 10.1007/s00228-018-2414-8. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29340733
-
[Population pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in Chinese children with epilepsy].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Apr;10(2):105-9. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18433522 Chinese.
-
Population pharmacokinetic models of lamotrigine in different age groups of Chinese children with epilepsy.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;73(4):445-453. doi: 10.1007/s00228-016-2190-2. Epub 2017 Jan 7. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28064355
-
Correlating lamotrigine serum concentrations with tolerability in patients with epilepsy.Neurology. 2004 Sep 28;63(6):1022-6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000138424.33979.0c. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15452293 Review.
-
Sources of lamotrigine pharmacokinetic variability: A systematic review of population pharmacokinetic analyses.Seizure. 2020 Nov;82:133-147. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Seizure. 2020. PMID: 33060011
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic interactions and dosing rationale for antiepileptic drugs in adults and children.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;84(1):97-111. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13400. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28815754 Free PMC article.
-
Authors' Reply to Standing et al.: "Effect of Age-Related Factors on the Pharmacokinetics of Lamotrigine and Potential Implications for Maintenance Dose Optimisation in Future Clinical Trials".Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Nov;57(11):1473-1475. doi: 10.1007/s40262-018-0698-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 30027512 No abstract available.
-
Pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine and its metabolite N-2-glucuronide: Influence of polymorphism of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and drug transporters.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;82(2):399-411. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12984. Epub 2016 May 29. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27096250 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Age-Related Factors on the Pharmacokinetics of Lamotrigine and Potential Implications for Maintenance Dose Optimisation in Future Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Aug;57(8):1039-1053. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0614-5. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29363050
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of new-generation antiepileptic drugs at the extremes of age: an update.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 Aug;52(8):627-45. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0067-4. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23640503 Review.
References
-
- Mullens EL. Clinical experience with lamotrigine monotherapy in adults with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Clin Drug Invest. 1998;16:125–33. - PubMed
-
- Biton V, Sackellares JC, Vuong A, Hammer AE, Barrett PS, Messenheimer JA. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of lamotrigine in primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Neurology. 2005;65:1737–43. - PubMed
-
- Goa K, Ross SR, Chrisp P. Lamotrigine. A review of its pharmacological proper ties and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs. 1993;46:152–76. - PubMed
-
- Chong E, Dupuis LL. Therapeutic drug monitoring of lamotrigine. Ann Pharmacother. 2002;36:917–20. - PubMed

