Layered reward signalling through octopamine and dopamine in Drosophila
- PMID: 23103875
- PMCID: PMC3528794
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11614
Layered reward signalling through octopamine and dopamine in Drosophila
Abstract
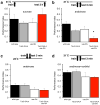
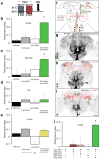
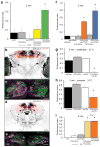
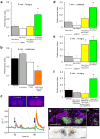
Dopamine is synonymous with reward and motivation in mammals. However, only recently has dopamine been linked to motivated behaviour and rewarding reinforcement in fruitflies. Instead, octopamine has historically been considered to be the signal for reward in insects. Here we show, using temporal control of neural function in Drosophila, that only short-term appetitive memory is reinforced by octopamine. Moreover, octopamine-dependent memory formation requires signalling through dopamine neurons. Part of the octopamine signal requires the α-adrenergic-like OAMB receptor in an identified subset of mushroom-body-targeted dopamine neurons. Octopamine triggers an increase in intracellular calcium in these dopamine neurons, and their direct activation can substitute for sugar to form appetitive memory, even in flies lacking octopamine. Analysis of the β-adrenergic-like OCTβ2R receptor reveals that octopamine-dependent reinforcement also requires an interaction with dopamine neurons that control appetitive motivation. These data indicate that sweet taste engages a distributed octopamine signal that reinforces memory through discrete subsets of mushroom-body-targeted dopamine neurons. In addition, they reconcile previous findings with octopamine and dopamine and suggest that reinforcement systems in flies are more similar to mammals than previously thought.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reward: Finding the paths to food reward.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Dec;13(12):816. doi: 10.1038/nrn3397. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23165253 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dayan P, Balleine BW. Reward, motivation, and reinforcement learning. Neuron. 2002;36:285–298. - PubMed
-
- Wise RA. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:483–494. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, et al. A subset of dopamine neurons signals reward for odour memory in Drosophila. Nature. 2012 - PubMed
-
- Hammer M. An identified neuron mediates the unconditioned stimulus in associative olfactory learning in honeybees. Nature. 1993;366:59–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

