Autozygome-guided exome sequencing in retinal dystrophy patients reveals pathogenetic mutations and novel candidate disease genes
- PMID: 23105016
- PMCID: PMC3561865
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.144105.112
Autozygome-guided exome sequencing in retinal dystrophy patients reveals pathogenetic mutations and novel candidate disease genes
Abstract
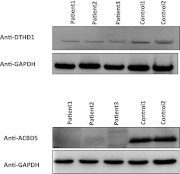
Retinal dystrophy (RD) is a heterogeneous group of hereditary diseases caused by loss of photoreceptor function and contributes significantly to the etiology of blindness globally but especially in the industrialized world. The extreme locus and allelic heterogeneity of these disorders poses a major diagnostic challenge and often impedes the ability to provide a molecular diagnosis that can inform counseling and gene-specific treatment strategies. In a large cohort of nearly 150 RD families, we used genomic approaches in the form of autozygome-guided mutation analysis and exome sequencing to identify the likely causative genetic lesion in the majority of cases. Additionally, our study revealed six novel candidate disease genes (C21orf2, EMC1, KIAA1549, GPR125, ACBD5, and DTHD1), two of which (ACBD5 and DTHD1) were observed in the context of syndromic forms of RD that are described for the first time.
Figures
References
-
- Abu Safieh L, Aldahmesh MA, Shamseldin H, Hashem M, Shaheen R, Alkuraya H, Al Hazzaa SA, Al-Rajhi A, Alkuraya FS 2010. Clinical and molecular characterisation of Bardet-Biedl syndrome in consanguineous populations: The power of homozygosity mapping. J Med Genet 47: 236–241 - PubMed
-
- Adams NA, Awadein A, Toma HS 2007. The retinal ciliopathies. Ophthalmic Genet 28: 113–125 - PubMed
-
- Al-Rashed M, Abu Safieh L, Alkuraya H, Aldahmesh MA, Alzahrani J, Diya M, Hashem M, Hardcastle AJ, Al-Hazzaa SA, Alkuraya FS 2012. RP1 and retinitis pigmentosa: Report of novel mutations and insight into mutational mechanism. British J Ophthalmol 96: 1018–1022 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
