IgA response in preterm neonates shows little evidence of antigen-driven selection
- PMID: 23105134
- PMCID: PMC3681535
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103347
IgA response in preterm neonates shows little evidence of antigen-driven selection
Abstract
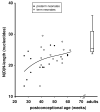
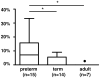
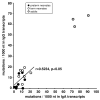
After birth, contact to environmental Ags induces the production of IgA, which represents a first line of defense for the neonate. We sought to characterize the maturation of the repertoire of IgA H chain transcripts in circulating blood B cells during human ontogeny. We found that IgA H chain transcripts were present in cord blood as early as 27 wk of gestation and that the restrictions of the primary Ab repertoire (IgM) persisted in the IgA repertoire. Thus, B cells harboring more "mature" V(H) regions were not preferred for class switch to IgA. Preterm and term neonates expressed a unique IgA repertoire, which was characterized by short CDR-H3 regions, preference of the J(H) proximal D(H)7-27 gene segment, and very few somatic mutations. During the first postnatal months, these restrictions were slowly released. Preterm birth did not measurably accelerate the maturation of the IgA repertoire. At a postconceptional age of 60 wk, somatic mutation frequency of IgA H chain transcripts reached 25% of the adult values but still showed little evidence of Ag-driven selection. These results indicate that similar to IgG, the IgA repertoire expands in a controlled manner after birth. Thus, the IgA repertoire of the newborn has distinctive characteristics that differ from the adult IgA repertoire. These observations might explain the lower affinity and specificity of neonatal IgA Abs, which could contribute to a higher susceptibility to infections and altered responses to vaccinations, but might also prevent the development of autoimmune and allergic diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Corthesy B. Roundtrip ticket for secretory IgA: role in mucosal homeostasis? J. Immunol. 2007;178:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Ha SA, Tsuji M, Fagarasan S. Intestinal IgA synthesis: a primitive form of adaptive immunity that regulates microbial communities in the gut. Semin. Immunol. 2007;19:127–135. - PubMed
-
- Kramer DR, Cebra JJ. Early appearance of “natural” mucosal IgA responses and germinal centers in suckling mice developing in the absence of maternal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1995;154:2051–2062. - PubMed
-
- Crabbe PA, Nash DR, Bazin H, Eyssen H, Heremans JF. Immunohistochemical observations on lymphoid tissues from conventional and germ-free mice. Lab. Invest. 1970;22:448–457. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Spoerri I, Schopfer JF, Nembrini C, Merky P, Massacand J, Urban JF, Jr., Lamarre A, Burki K, Odermatt B, Zinkernagel RM, Macpherson AJ. Mechanisms of neonatal mucosal antibody protection. J. Immunol. 2006;177:6256–6262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

