Rectal hyposensitivity
- PMID: 23105997
- PMCID: PMC3479250
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2012.18.4.373
Rectal hyposensitivity
Abstract
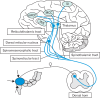
Impaired or blunted rectal sensation, termed rectal hyposensitivity (RH), which is defined clinically as elevated sensory thresholds to rectal balloon distension, is associated with disorders of hindgut function, characterised primarily by symptoms of constipation and fecal incontinence. However, its role in symptom generation and the pathogenetic mechanisms underlying the sensory dysfunction remain incompletely understood, although there is evidence that RH may be due to 'primary' disruption of the afferent pathway, 'secondary' to abnormal rectal biomechanics, or to both. Nevertheless, correction of RH by various interventions (behavioural, neuromodulation, surgical) is associated with, and may be responsible for, symptomatic improvement. This review provides a contemporary overview of RH, focusing on diagnosis, clinical associations, pathophysiology, and treatment paradigms.
Keywords: Constipation; Fecal incontinence; Rectal hyposensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Azpiroz F, Bouin M, Camilleri M, et al. Mechanisms of hypersensitivity in IBS and functional disorders. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007;19:62–88. - PubMed
-
- Palit S, Lunniss PJ, Scott SM. The physiology of human defecation. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:1445–1464. - PubMed
-
- Mertz H, Naliboff B, Munakata J, Niazi N, Mayer EA. Altered rectal perception is a biological marker of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:40–52. - PubMed
-
- Poitras P, Riberdy Poitras M, Plourde V, Boivin M, Verrier P. Evolution of visceral sensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:914–920. - PubMed
-
- Farmer AD, Aziz Q. Visceral pain hypersensitivity in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Br Med Bull. 2009;91:123–136. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

