The mechanisms of nadroparin-mediated inhibition of proliferation of two human lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 23106301
- PMCID: PMC6495835
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00847.x
The mechanisms of nadroparin-mediated inhibition of proliferation of two human lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
Objectives: Clinical data suggest that heparin treatment improves survival of lung cancer patients, but the mechanisms involved are not fully understood. We investigated whether low molecular weight heparin nadroparin, directly affects lung cancer cell population growth in conventionally cultured cell lines.
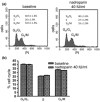
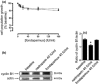
Materials and methods: A549 and CALU1 cells' viability was assessed by MTT and trypan blue exclusion assays. Cell proliferation was assessed using 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine incorporation. Apoptosis and cell-cycle distribution were analysed by flow cytometry; cyclin B1, Cdk1, p-Cdk1 Cdc25C, p-Cdc25C and p21 expressions were analysed by western blotting. mRNA levels were analysed by real time RT-PCR.
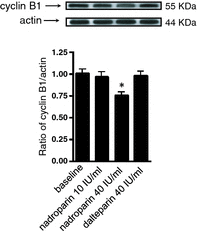
Results: Nadroparin inhibited cell proliferation by 30% in both cell lines; it affected the cell cycle in A549, but not in CALU-1 cells, inducing arrest in the G(2) /M phase. Nadroparin in A549 culture inhibited cyclin B1, Cdk1, Cdc25C and p-Cdc25C, while levels of p-Cdk1 were elevated; p21 expression was not altered. Dalteparin caused a similar reduction in A549 cell population growth; however, it did not alter cyclin B1 expression as expected, based on previous reports. Fondaparinux caused minimal inhibition of A549 cell population growth and no effect on either cell cycle or cyclin B1 expression.
Conclusions: Nadroparin inhibited proliferation of A549 cells by inducing G(2) /M phase cell-cycle arrest that was dependent on the Cdc25C pathway, whereas CALU-1 cell proliferation was halted by as yet not elucidated modes.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures







References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J. Clin. 59, 225–249. - PubMed
-
- Molina JR, Adjei AA, Jett JR (2006) Advances in chemotherapy of non‐small cell lung cancer. Chest 130, 1211–1219. - PubMed
-
- Kakkar AK, Levine MN, Kadziola Z, Lemoine NR, Low V, Patel HK et al (2004) Low molecular weight heparin, therapy with dalteparin, and survival in advanced cancer: the fragmin advanced malignancy outcome study (FAMOUS). J. Clin. Oncol. 22, 1944–1948. - PubMed
-
- Altinbas M, Coskun HS, Er O, Ozkan M, Eser B, Unal A et al (2004) A randomized clinical trial of combination chemotherapy with and without low‐molecular‐weight heparin in small cell lung cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2, 1266–1271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

